Earlier this year, 16 states and the District of Columbia submitted plans for implementing the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) to the Department of Education, detailing strategies to strengthen standards, accountability, teacher effectiveness and student supports. Since then, the remaining 34 states have continued work drafting their own plans. Despite uncertainty from Washington, DC, states such as New York and California are taking advantage of ESSA’s increased flexibility to promote career readiness, specifically through new accountability systems.
Despite lawmakers’ intentions to expand local flexibility, state planning has been somewhat constrained by the federal budget process. In May, Congress approved a budget for Fiscal Year 2017 that fell short of the authorized funding for certain ESSA programs. Specifically, the Title IV-A Student Support and Academic Enrichment (SSAE) grant program — which consolidated a basket of categorically-funded initiatives in order to expand state flexibility — was funded at only $400 million for the year, far short of the authorized $1.6 billion (the program is eliminated entirely under the President’s proposed FY18 budget). As such, lawmakers decided to give states the option to distribute grants competitively rather than through a formula, as is prescribed in the law. It is not year clear if states will take this opportunity, though switching to a competition may discourage smaller districts from applying.
Under ESSA, at least 95 percent of SSAE funds are to be awarded to local education agencies for one of three priorities: supporting a well-rounded education, fostering a safe and healthy school climate and providing for the effective use of technology. These funds can be used to strengthen or enhance local Career Technical Education (CTE) programs, which are covered under the statutory definition of “well-rounded education.” Although funds go primarily to the local level, states have leeway to signal how they should be used. They can also expend state set-aside funds under Title IV-A to administer technical assistance in certain priority areas. While SSAE grants provide a clear leverage point to promote CTE statewide, many states are approaching the opportunity with caution, leaving it up to local education agencies to determine how such funds will be spent.
In the Wake of April’s Submission Window, Five States — Including New York and California — Release Draft Plans
In addition to the 16 states and D.C. that submitted plans during the first window, another 20 states have released draft plans or guidelines as of June 2017. The newest states to release draft plans include Arkansas, California, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New York, Rhode Island and Wisconsin. Below we examine different approaches that New York and California are taking to leverage ESSA in support of statewide career readiness.
New York’s Plan Envisions Success in College, Careers and Citizenship
 Building on the state’sgraduation pathways work, one of the key threads throughout New York’s first ESSA state plan draft is ensuring all students graduate “prepared for success in postsecondary education, careers, and citizenship.” The plan envisions a K-12 system that provides rigorous instruction, positive learning environments, and appropriate opportunities and supports so that all students can succeed.
Building on the state’sgraduation pathways work, one of the key threads throughout New York’s first ESSA state plan draft is ensuring all students graduate “prepared for success in postsecondary education, careers, and citizenship.” The plan envisions a K-12 system that provides rigorous instruction, positive learning environments, and appropriate opportunities and supports so that all students can succeed.
One area in the plan where this priority is reflected is the state’s accountability system, which adopts a measure of College, Career and Civic Readiness as one of two School Quality and Student Success indicators at the high school level. ESSA requires states to adopt at least five accountability indicators, four that are loosely prescribed and a fifth measure of school quality that is up to a state’s choosing. As we’ve reported in the past, many states are seizing the opportunity to measure not only college preparedness but career readiness as well.
In New York’s case, the proposed College, Career and Civic Readiness Index encourages both college and career preparation and awards bonus points for students who surpass the minimum Regents or Local Diploma requirements. Under the proposal, schools will receive full points for students who earn a standard diploma, an additional half point for students who enroll in Advanced Placement (AP), International Baccalaureate (IB) or dual credit courses, and a full two points for students earning a CTE endorsement, an industry-recognized credential or a passing score on an AP or IB exam (among other options).
Furthermore, the plan explicitly encourages local education agencies to use SSAE grants to offer multiple pathways to graduation and career readiness. The state plans to use up to 4 percent of its permitted set-aside funds to support local education agencies to implement this, and other, priorities. And while the plan is light on details, the state promises to support student access to extra-curricular opportunities, including “community-based internships and … sports and arts.” New York’s state plan is still in the public comment stage and subject to change prior to the September submission deadline.
In California, Local Control Accountability Plans Will Drive ESSA Implementation
 California meanwhile is approaching ESSA’s increased flexibility as an opportunity to supplement ongoing state efforts. In 2013, the Golden State transformed the way it funds education using a Local Control Funding Formula (LCFF) to consolidate state education funding and empower local education agencies to create and implement their own strategic priorities. Under the policy, local districts are required to create Local Control Accountability Plans (LCAP) to set goals and plan their delivery strategies. Additionally, California last year adopted a new multi-measure accountability system aligned to the LCFF to hold local districts accountable for using state education funds effectively. Just this year the state Department of Education released a school accountability dashboard that illustrates student performance on a variety of different measures.
California meanwhile is approaching ESSA’s increased flexibility as an opportunity to supplement ongoing state efforts. In 2013, the Golden State transformed the way it funds education using a Local Control Funding Formula (LCFF) to consolidate state education funding and empower local education agencies to create and implement their own strategic priorities. Under the policy, local districts are required to create Local Control Accountability Plans (LCAP) to set goals and plan their delivery strategies. Additionally, California last year adopted a new multi-measure accountability system aligned to the LCFF to hold local districts accountable for using state education funds effectively. Just this year the state Department of Education released a school accountability dashboard that illustrates student performance on a variety of different measures.
California’s state plan proposes to use LCFF as a vehicle to implement ESSA. The plan, appropriately titled “The California Way,” proposes to map local ESSA planning efforts against the current LCAP to create a “single, coherent system that avoids the complexities of having separate state and federal accountability structures.” Local education agencies will submit an LCAP addendum as a supplement to address additional requirements under ESSA.
So how will California’s ESSA plan support career readiness? For one, the current accountability system includes a career and college readiness index. Interestingly, and unlike most other state proposals thus far, the index will count toward the state’s academic success indicator, along with student performance and growth on assessments. While the State Board of Education has blessed the indicator, it has yet to determine how it will be measured. Current considerations include dual enrollment, AP exam performance, IB exam performance and CTE pathway completion. Additionally, California’s plan points to other recent initiatives — such as the state’s three-year, $900 million CTE Incentive Grant Program — that are designed to enhance and expand regional CTE pathways in the state.
What New York’s and California’s ESSA state plans tell us is that states are taking full advantage of newfound flexibility to align federal initiatives with their own efforts. In the case of California and New York, both states have undergone work in recent years to revise graduation and accountability policy to better promote career readiness in high school. Others should consider how to align opportunities under ESSA to support their own state and local initiatives.
Austin Estes, Policy Associate
![]()


 The demand for Bachelor’s degrees may be
The demand for Bachelor’s degrees may be  In Vermont, Governor Phil Scott announced the launch of a new initiative called
In Vermont, Governor Phil Scott announced the launch of a new initiative called  A little over one year ago, Advance CTE launched
A little over one year ago, Advance CTE launched  In order to deliver high-quality CTE for all learners, state systems must work together at every level. Secondary and postsecondary must work together and with agencies that handle workforce and economic development issues. All of those agencies must also engage with employer partners and local districts and institutions to inform the design, validation and implementation of CTE programs.
In order to deliver high-quality CTE for all learners, state systems must work together at every level. Secondary and postsecondary must work together and with agencies that handle workforce and economic development issues. All of those agencies must also engage with employer partners and local districts and institutions to inform the design, validation and implementation of CTE programs.  Putting Learner Success First: A Shared Vision for the Future of CTE
Putting Learner Success First: A Shared Vision for the Future of CTE Building on the state’s
Building on the state’s California meanwhile is approaching ESSA’s increased flexibility as an opportunity to supplement ongoing state efforts. In 2013, the Golden State transformed the way it funds education using a
California meanwhile is approaching ESSA’s increased flexibility as an opportunity to supplement ongoing state efforts. In 2013, the Golden State transformed the way it funds education using a  In the nine months since President Obama signed the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) into law last December, states and policymakers have been hard at work digging through the legislation and deciding how to structure their new plans. ESSA, which reauthorized the Elementary and Secondary Education Act, presents a number of opportunities to expand access to high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). As states prepare to implement the law next year, we will provide periodic updates on their progress and share strategies for leveraging ESSA to support CTE at the state level.
In the nine months since President Obama signed the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) into law last December, states and policymakers have been hard at work digging through the legislation and deciding how to structure their new plans. ESSA, which reauthorized the Elementary and Secondary Education Act, presents a number of opportunities to expand access to high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). As states prepare to implement the law next year, we will provide periodic updates on their progress and share strategies for leveraging ESSA to support CTE at the state level. A
A 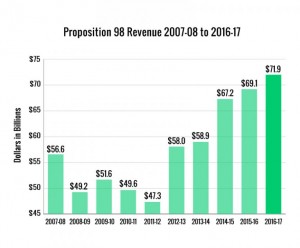 With students now on summer vacation, policymakers have been hard at work preparing for the upcoming school year – and Career Technical Education (CTE) has been front and center in several states. Last month, California approved a massive budget, including funds for the CTE Pathways Program and the new Strong Workforce Program. Meanwhile, some states are exploring strategies to address teacher shortages.
With students now on summer vacation, policymakers have been hard at work preparing for the upcoming school year – and Career Technical Education (CTE) has been front and center in several states. Last month, California approved a massive budget, including funds for the CTE Pathways Program and the new Strong Workforce Program. Meanwhile, some states are exploring strategies to address teacher shortages.