Advance CTE released the 2023 State of CTE: An Analysis of State Secondary CTE Funding Models to highlight how states and the District of Columbia provide high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE) through various secondary CTE funding models and approaches. This blog, the fourth in a series, describes ways states invest in CTE programs through line item appropriations to support unique elements of CTE. This blog unveils new information not available in the State of CTE Funding release.
Overview
 States make significant contributions to CTE programs through non-categorical, line item appropriations. Programmatic funding is distributed through periodic, legislatively established authorizations that are contingent on the availability of funds. States often place conditions on how money should be spent or used to promote state priorities. Additionally, a programmatic line item appropriation can be a recurring or a one-time investment. This blog highlights appropriations in industry-recognized credentials, Career Technical Student Organizations (CTSOs), career advisement, and educator preparation for fiscal year (FY) 2022. You can read more about categorical funding in the first blog in this series, Funding Career Technical Education: Secondary CTE Funding Basics.
States make significant contributions to CTE programs through non-categorical, line item appropriations. Programmatic funding is distributed through periodic, legislatively established authorizations that are contingent on the availability of funds. States often place conditions on how money should be spent or used to promote state priorities. Additionally, a programmatic line item appropriation can be a recurring or a one-time investment. This blog highlights appropriations in industry-recognized credentials, Career Technical Student Organizations (CTSOs), career advisement, and educator preparation for fiscal year (FY) 2022. You can read more about categorical funding in the first blog in this series, Funding Career Technical Education: Secondary CTE Funding Basics.
These key state investments often pilot new programs, sustain existing programs, provide training to educators and professionals, or allow purchases for needed equipment and supplies. These investments certainly allow Local Education Agencies (LEAs) to scale and improve program quality, which aligns with Advance CTE’s vision for the future of CTE where continuous improvement is needed at all levels within systems.
Investing in Unique Elements of CTE
State funding through non-categorical, line item appropriations is incredibly common; 80 percent of state leaders surveyed in summer 2022 reported some line items for CTE programs.
Industry-recognized Credentials
Helping learners have access to and earn industry-recognized credentials can make them more competitive for future work and educational opportunities. States may offer reimbursements to the learner, educator, or local institutions for the completion of credentials. There are expenses associated with industry-recognized credentials such as exam fees, materials, books, or supplies.
Thirteen state leaders reported appropriations for industry-recognized credentials in FY 2022.
- Indiana enacted H.B. 1001 and appropriated $200,000 to the Governor’s Workforce Cabinet to help cover the expenses for earning industry-recognized credentials.
- Ohio appropriated $8 million for credential reimbursements to districts and $12.5 million for the Innovative Workforce Incentive Program through H.B. 110, which awards districts, community schools, STEM schools, and joint vocational school districts $1,250 for each credential a student earns from a list of priority credentials established by the Governor’s Office of Workforce Transformation.
CTSOs
CTSOs allow learners to gain academic, workplace, and technical skills, build networks, and pursue leadership experiences that are needed to succeed in today’s global workforce.
Twelve state leaders reported line item appropriations for CTSOs, with appropriations ranging from $125,000 to $2.52 million per year in FY 2022. Most states allocated the funds toward one or more of the 11 CTSOs specifically authorized in the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act (Perkins V).
- South Carolina allowed funds through H. 4100 for a Career Cluster Partnership Program to be used for organizations’ statewide student competitions leading to national competitions.
Career Advisement
Offering comprehensive and connected career advisement systems helps all learners get the support and guidance to gain skills and explore future careers.
Nine state leaders reported line item appropriations for career advisement in FY 2022.
- Connecticut’s Career Resource Network and Massachusetts’ My Career and Academic Plan (MyCAP) are two examples of career resources that have been funded across multiple years.
Other states have made one-time investments to help pilot programs and offerings.
- North Carolina enacted S.B. 105 and appropriated $1.5 million in non-recurring funds to use a ScholarPath platform to create a 12th-grade transition pilot program. The program is an education planning and communication platform that helps learners and their families use O*NET data to connect and match learners to high-demand careers.
Other states focused on providing resources for professionals who help with career advisement and planning.
- Arkansas appropriated $6.31 million toward a career coaches public school fund and program grants for career education services for students with special needs through H.B. 1167.
CTE Educator Preparation
There remains room for improvement in CTE educator preparation as only Georgia, Minnesota, and Virginia reported line item appropriations for CTE educator preparation in FY 2022.
- Minnesota enacted S.F.No.9 and provided $400,000 to the Minnesota State Colleges and Universities System for a CTE educator pilot project.
- Virginia’s H.B.1800 appropriated $1.3 million for information technology (IT) industry certifications, which included the use of funds to increase the number of teachers in targeted CTE areas and teachers who receive training in IT and industry-recognized certifications.
You can learn more about identifying funding streams that support CTE educator diversity by reading Advance CTE’s State and Local Strategies for Diversifying the CTE Educator Workforce.
Recommendations
Programmatic line item appropriations are additional sources of funding to leverage to support important components of career preparation ecosystems. State leaders should take the following action steps:
- Tell the story of state investment in CTE at the local level so LEAs can best leverage resources across funding streams. Although most states provide funding for secondary CTE, due to a lack of sufficient state-level accountability and data collection, states do not have lines of sight into how LEAs are using funds. Therefore, measuring the impact of state funding and advocating for evolution in either the structure or levels of state funding is challenging.
- Review federal, state, and local funding sources, including the purpose, population it will serve, and eligibility requirements. Identify manuals or documents that explain the allowable use cases for the state funding streams. Explore how to braid the funding with other resources to get the most value for CTE investments.
- Establish a sustainability plan to navigate shifts in funding. These programmatic line item appropriations may be one-time investments. Having a plan in place to offer continuity of high-quality CTE programs and services will ease the barrier of loss of funding.
 Additional Resources
Additional Resources
Be sure to read the other blogs in this series:
- Funding Career Technical Education: Secondary CTE Funding Basics,
- Funding Career Technical Education: Using the 2023 State of CTE Funding Report Resources, and
- Funding Career Technical Education: Incorporating Elements Into Funding Models to Address CTE Access, Completion and Program Quality.
We also encourage you to watch the Exploring State Secondary CTE Funding webinar.
Dr. Laura Maldonado, Senior Research Associate
Dr. Laura Maldonado is a Senior Research Associate with Advance CTE. In this role, Laura directly supports Advance CTE’s policy research and technical assistance initiatives, data quality initiatives and internal data strategy.


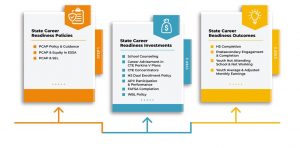 In May, the Coalition for Career Development Center released the first annual
In May, the Coalition for Career Development Center released the first annual 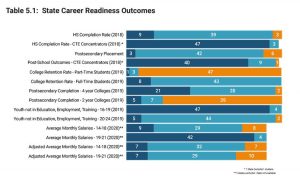 For postsecondary CTE concentrators, the report finds that 40 states are placing 70 percent or more of secondary learners into postsecondary training and education, military or employment after high school graduation. Only three states, however, are placing 70 percent or more of all high school graduates into either a two-year or four-year postsecondary training or education program. The report recommends expanding post-school data points as well as counting military service and employment as post-school outcomes for learners.
For postsecondary CTE concentrators, the report finds that 40 states are placing 70 percent or more of secondary learners into postsecondary training and education, military or employment after high school graduation. Only three states, however, are placing 70 percent or more of all high school graduates into either a two-year or four-year postsecondary training or education program. The report recommends expanding post-school data points as well as counting military service and employment as post-school outcomes for learners. Today, Advance CTE released a
Today, Advance CTE released a  One presentation I moderated was a conversation with state and local leaders based on Advance CTE research regarding the importance of
One presentation I moderated was a conversation with state and local leaders based on Advance CTE research regarding the importance of 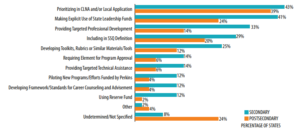
 Career Technical Education (CTE) is gaining widespread interest and support from state policymakers, who see it as a strategy to expand access to opportunity and meet employer needs. Between 2014 and 2018, states
Career Technical Education (CTE) is gaining widespread interest and support from state policymakers, who see it as a strategy to expand access to opportunity and meet employer needs. Between 2014 and 2018, states 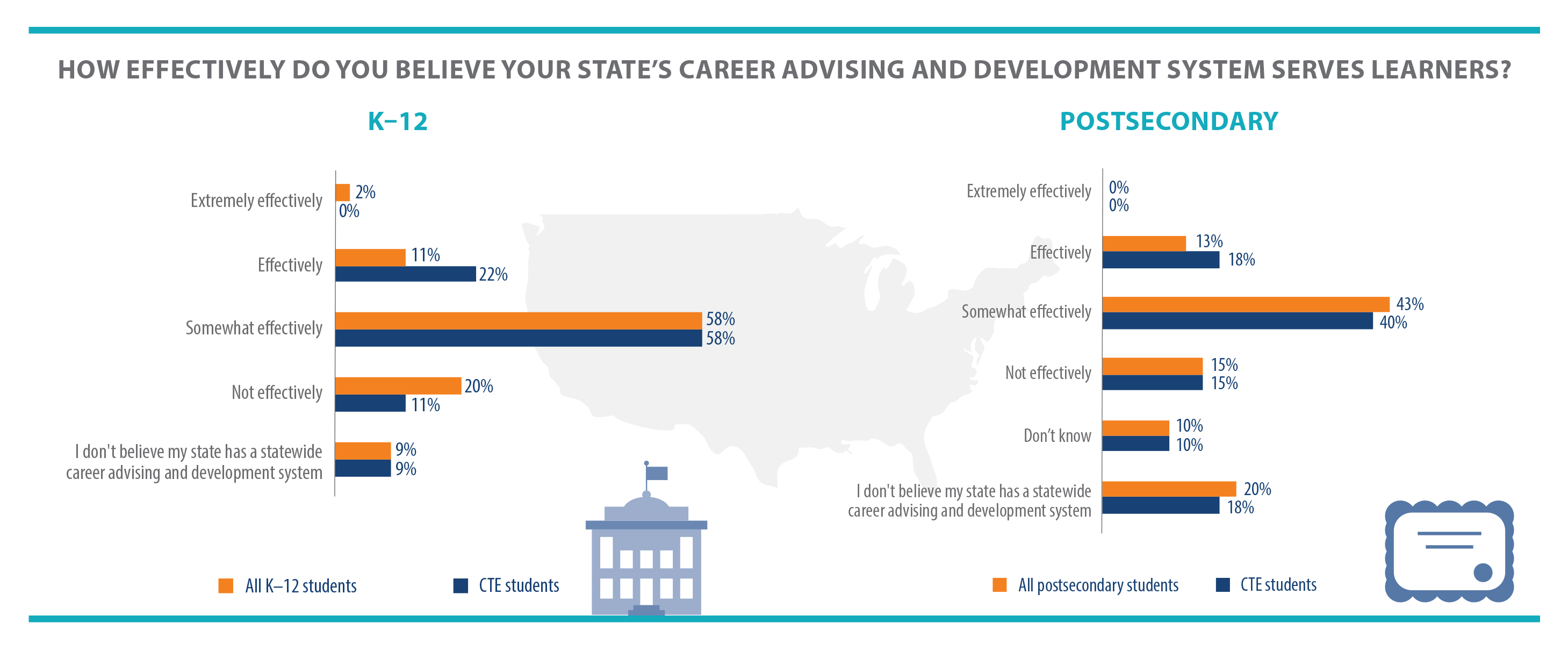
 A little over one year ago, Advance CTE launched
A little over one year ago, Advance CTE launched  Career exploration and guidance have in the past been considered as services only for CTE students, and particularly for CTE students who are not considering attending a postsecondary institution. Now state leaders are working to change this misconception by promoting career advisement as an integral part of the educational process for all learners.
Career exploration and guidance have in the past been considered as services only for CTE students, and particularly for CTE students who are not considering attending a postsecondary institution. Now state leaders are working to change this misconception by promoting career advisement as an integral part of the educational process for all learners.  school is an excellent time to explore different careers and take introductory CTE courses. The report goes on to describe six recommendations, which are listed in the graphic on the right, for effective career counseling programs and dives into some of the barriers middle schools can face in providing students with quality career exploration experiences. Though many of the recommendations are focused at the local level, the authors note that state leaders have an important role to play in supporting these local innovations and practices.
school is an excellent time to explore different careers and take introductory CTE courses. The report goes on to describe six recommendations, which are listed in the graphic on the right, for effective career counseling programs and dives into some of the barriers middle schools can face in providing students with quality career exploration experiences. Though many of the recommendations are focused at the local level, the authors note that state leaders have an important role to play in supporting these local innovations and practices.