 This week the Senate confirmed Dr. Amy Loyd to be the next head of the federal office overseeing Career Technical Education (CTE) while U.S. Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona testified about the Administration’s federal fiscal year 2023 (FY23) budget request as his Department convened an event on learner pathways.
This week the Senate confirmed Dr. Amy Loyd to be the next head of the federal office overseeing Career Technical Education (CTE) while U.S. Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona testified about the Administration’s federal fiscal year 2023 (FY23) budget request as his Department convened an event on learner pathways.
Senate Confirms New OCTAE Leader
On Wednesday, June 8, the Senate voted 57-42 to confirm Dr. Amy Loyd to be the next Assistant Secretary for Career, Technical, and Adult Education. In this position Dr. Loyd will lead the Office of Career, Technical, and Adult Education (OCTAE) within the U.S. Department of Education (ED)—a posting that oversees CTE, including the implementation of the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act (Perkins V). Following the vote, Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona issued a statement saying, in part, “I am thrilled by the Senate’s confirmation of Amy Loyd, whose expertise in the intersection between education and workforce development will make her an excellent assistant secretary [of OCTAE].” Following the confirmation vote Wednesday evening, Advance CTE and the Association of Career and Technical Education (ACTE) published a joint statement of support:
“As key legislation and funding negotiations with implications for Career Technical Education (CTE) and workforce development persist in Congress, it is crucial for leaders at the intersection of education and work to have a seat at the table. Dr. Loyd’s confirmation as OCTAE Assistant Secretary provides the field with an exceptional advocate for equitable access to high-quality CTE and an experienced leader with a deep understanding of not only the needs of local, regional and state CTE leaders, but also historically marginalized communities through her work at JFF and the Cook Inlet Tribal Council in Alaska. Her leadership at OCTAE will be instrumental in preparing our nation’s workforce to obtain and advance in high-skill, high-wage and in-demand careers. We congratulate Assistant Secretary Loyd on her confirmation, and look forward to working with her to ensure federal policy fully leverages CTE programs and career pathways as high-quality, equitable avenues for each learner to achieve success in the jobs of the future.”
Advance CTE looks forward to working with Assistant Secretary Loyd in this capacity to advance the organization’s federal policy priorities and ensure strong CTE leadership within ED moving forward.
Cardona Testifies on Budget as FY23 Funding Efforts Move Forward
On Tuesday, June 7, the Senate Committee on Appropriations’ Labor, Health, and Human Services, Education and Related Agencies Subcommittee hosted U.S. Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona to testify about the Administration’s fiscal year 2023 (FY23) budget request for the U.S. Department of Education. The hearing focused on a wide range of issues, including CTE which was touched on by both Senators Braun (R-IN) and Baldwin (D-WI) during questioning. Sen. Baldwin in particular noted that the Administration’s proposed “career connected high schools” initiative would serve only a small subset of communities throughout the nation and asked how ED planned to ensure that support for high-quality CTE programs would be made available to a greater number of states by supplementing, rather than supplanting, existing federal support for CTE. Cardona answered, in part, that ED plans to “. . . continue to advocate and find ways to support [CTE] programs and find ways to make whatever new money is available eligible to those who are already doing this work.” An archived webcast of the hearing, including Secretary Cardona’s testimony, can be accessed here.
In other FY23 funding news, Sens. Blumenthal (D-CT), Baldwin (D-WI), and Kaine (D-VA) recently led a Dear Colleague letter in support of robust funding for Perkins V’s basic state grant program. This letter garnered the support of 38 Senators and was shared with Senate appropriations leadership as the FY23 funding process gets underway in the chamber. Meanwhile, lawmakers in the House advanced a key procedural measure this week to begin debate on the 12 individual appropriations bills that compose the federal discretionary budget. This measure sets an overall $1.6 trillion budget limit for FY23—the same amount that was requested in President Biden’s most recent budget request—which will allow appropriators to begin to allocate this proposed amount among forthcoming spending bills. Advance CTE expects this work to begin later this month, likely beginning next week, ahead of the July 4th Congressional recess. As these efforts get underway, we will continue to advocate for a robust investment in Perkins V’s basic state grant program to meet the significant funding needs of the CTE community.
Career Connected Learning Event
Last week, June 1, ED convened a virtual event with U.S. Secretary of Labor Marty Walsh and U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo to discuss the Department’s new “career connected high schools” initiative proposed as part of the Administration’s FY23 budget request. The event also featured remarks from U.S. Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona, who shared the Administration’s wider career connected learning strategy moving forward which will focus on five core pillars:
- An overarching belief that every student should have a pathway to college and the preparation they need to get a head start while still in high school;
- Work-based learning to help students gain real-world knowledge, skills, exposure, and learning experience they’ll need to enter and succeed in careers;
- Industry credentials to help students make progress to earning in-demand, industry-recognized credentials that can give them a leg up in today’s workforce and launch careers more quickly;
- College and career advising and navigation to equip students with better information to make thoughtful decisions and lay groundwork for what comes after high school; and
- Systems, strategies, and capacity building to create a system that eliminates transition barriers and creates new capacities to support student success.
An archive of the event, including additional information, can be found here.
Steve Voytek, Policy Advisor


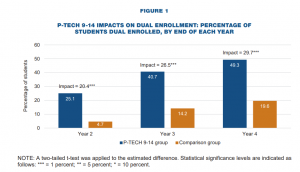 What findings from the Bridging of the School-to-Work Divide and the On-Ramp to College studies, would you highlight for state CTE leaders in particular
What findings from the Bridging of the School-to-Work Divide and the On-Ramp to College studies, would you highlight for state CTE leaders in particular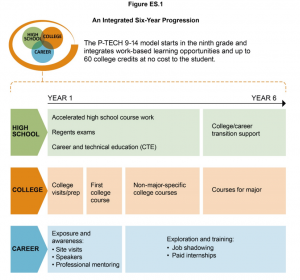
 “Go forth without limits!” was an apt parting chat message as over 70 state Career Technical Education (CTE) leaders from across 16 states convened virtually last month to launch the community of practice for
“Go forth without limits!” was an apt parting chat message as over 70 state Career Technical Education (CTE) leaders from across 16 states convened virtually last month to launch the community of practice for  Vargas challenged attendees to dream big and be the new models for scalable solutions by being a “network facilitator,” by combining career pathway expansion with intentional investments in collaboration and sustained partnershi
Vargas challenged attendees to dream big and be the new models for scalable solutions by being a “network facilitator,” by combining career pathway expansion with intentional investments in collaboration and sustained partnershi In support of this effort, Advance CTE recently published
In support of this effort, Advance CTE recently published 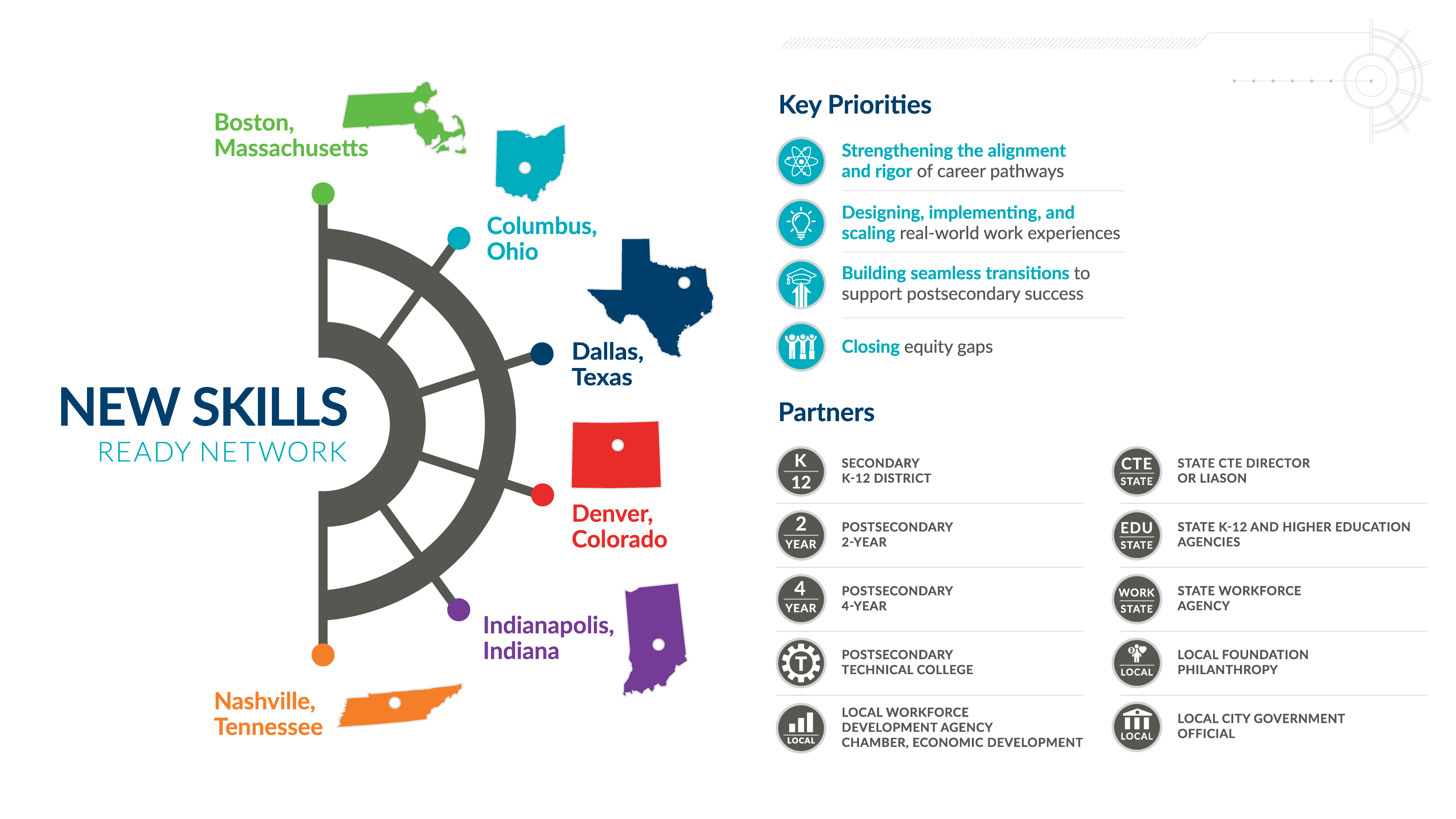
 Today, Advance CTE and Education Strategy Group (ESG) released an
Today, Advance CTE and Education Strategy Group (ESG) released an 
 Intentional and early collaboration between state and local leaders is vital to ensuring success in high-quality career pathways for all learners.
Intentional and early collaboration between state and local leaders is vital to ensuring success in high-quality career pathways for all learners. 
