 By now the consensus in the education community is clear: in addition to a strong academic foundation, students should be able to access other experiences in high school — physical education, the arts, Career Technical Education (CTE) — that provide added value to their education and increase the likelihood of postsecondary success.
By now the consensus in the education community is clear: in addition to a strong academic foundation, students should be able to access other experiences in high school — physical education, the arts, Career Technical Education (CTE) — that provide added value to their education and increase the likelihood of postsecondary success.
The notion that high schools should provide a “well-rounded education” was codified in the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) in 2015. The law, which Congress passed with bipartisan support, provides several opportunities for integrating CTE and other well-rounded learning opportunities into the traditional high school experience, which Advance CTE has covered extensively on this blog and in our publications. More than four years after the law was passed, some states have begun to leverage these opportunities to advance career readiness in high school.
Expanding Opportunities for Each Child in Ohio
One often overlooked opportunity in ESSA is the Direct Student Services (DSS) provision. DSS allows states to set aside up to 3 percent of their basic Title I grants to help local education agencies expand access to advanced coursework and CTE. Only two states — Louisiana and New Mexico — opted to use the allowance in their submitted ESSA plans. But they were soon joined by Ohio, which decided in 2018 to leverage the DSS allowance to launch a new grant program called Expanding Opportunities for Each Child.
The program has two primary objectives: developing and expanding access to career pathways that culminate in high-value credentials and promoting access and success in advanced coursework such as Advanced Placement (AP) and International Baccalaureate (IB). These objectives are aligned with Ohio’s strategic priorities for secondary education, which emphasize postsecondary readiness and preparation for college and career. Ohio’s decision to use the DSS allowance was based on the idea that freeing up additional resources would help local education agencies better support student achievement and transitions to post-high school pathways.
In July 2018, Ohio awarded more than $7.2 million in three-year grants to 17 recipients. Fourteen will be conducting career pathways development and three will be expanding access to AP and IB courses. A second round of applications is expected to be issued later in the 2018-19 school year.
Building Capacity for STEM Learning in Georgia
Though the Title IV Student Support and Academic Enrichment grant program, Congress authorized funding to the tune of $1.6 billion to enhance well-rounded education, school safety and the effective use of technology in schools. While the program has not been fully funded by Congress, it still provides significant resources to help schools deliver a well-rounded education, including CTE and Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) education.
While most states have left the determination of how to spend Title IV funds up to local leaders, some have issued guidance or put together trainings to help schools leverage their resources in service of statewide priorities for career readiness.
Georgia is one such example. In its ESSA plan, the state committed to using Title IV funds to strengthen school counseling, computer science and STEM. Since then, Georgia has used Title IV funds to hire two full-time STEM coordinators, one in the southwest region and one in the southeast region. The coordinators are working to build STEM learning opportunities for schools and strengthen STEM pipelines in their areas. Additionally, Georgia has allocated Title IV funds to develop an online STEM incubator learning pathway to help district and school leaders navigate the process for certifying STEM schools.
Curating CTE Open Educational Resources in Nebraska

 Another state that is using Title IV funds to boost career readiness is Nebraska. Leaders in the state are using Title IV funds to recruit CTE teachers to curate and develop educational resources aligned with college and career content area standards. This is a key feature of the state’s new Open Educational Resources (OER) Hub, which was launched in February 2019 and provides open access resources aligned with Nebraska’s college and career ready standards.
Another state that is using Title IV funds to boost career readiness is Nebraska. Leaders in the state are using Title IV funds to recruit CTE teachers to curate and develop educational resources aligned with college and career content area standards. This is a key feature of the state’s new Open Educational Resources (OER) Hub, which was launched in February 2019 and provides open access resources aligned with Nebraska’s college and career ready standards.
The work is still in the early stages, but Nebraska hopes to build out the CTE resources in the OER Hub later this summer by engaging CTE teachers to share, curate and develop rigorous digital resources that can be adopted and modified in the classroom. The state will provide stipends and cover travel expenses for participating CTE teachers. While this work is starting with three career areas — business, marketing, and management; communication and information systems; and human sciences and education — Nebraska plans to expand the resources to the remaining three state-identified career areas soon.
States made bold commitments in their ESSA plans to expand access to advanced coursework and career pathways. This is best demonstrated by the fact that 40 states are now measuring career readiness in their state and federal accountability systems. But few states are going the extra mile to align ESSA implementation with their plans for career readiness. Ohio, Georgia and Nebraska demonstrate three different approaches states can take to advance career readiness through ESSA.
Austin Estes, Senior Policy Associate


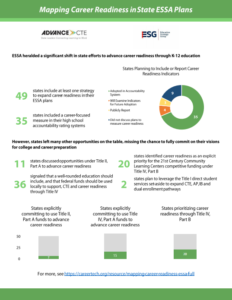 This year marked a pivotal moment for K-12 education. With the passage of the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) in 2015, state leaders have spent the last two years reexamining and strategizing they way they deliver K-12 education. Now that the last ESSA plans have been written and submitted, we finally have a national picture of state priorities for education, including how K-12 education systems will support and reinforce career preparation opportunities.
This year marked a pivotal moment for K-12 education. With the passage of the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) in 2015, state leaders have spent the last two years reexamining and strategizing they way they deliver K-12 education. Now that the last ESSA plans have been written and submitted, we finally have a national picture of state priorities for education, including how K-12 education systems will support and reinforce career preparation opportunities.  Building on the state’s
Building on the state’s California meanwhile is approaching ESSA’s increased flexibility as an opportunity to supplement ongoing state efforts. In 2013, the Golden State transformed the way it funds education using a
California meanwhile is approaching ESSA’s increased flexibility as an opportunity to supplement ongoing state efforts. In 2013, the Golden State transformed the way it funds education using a