The views, opinions, services and products shared in this post are solely for educational purposes and do not imply agreement or endorsement by Advance CTE, nor discrimination against similar brands, products or services not mentioned.
 In recent years, middle school career exploration has gained traction as a foundational element of Career Technical Education (CTE). As many State CTE Directors and leaders know, the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act (Perkins V), signed into law in July 2018, for the first time permitted Perkins funding to be used on career exploration programming as early as fifth grade. Here are four strategic actions that states can take to expand and enhance career exploration programs that prepare learners for postsecondary education and career success, based on a recent nationwide study of middle school career exploration programs, commissioned by American Student Assistance® (ASA).
In recent years, middle school career exploration has gained traction as a foundational element of Career Technical Education (CTE). As many State CTE Directors and leaders know, the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act (Perkins V), signed into law in July 2018, for the first time permitted Perkins funding to be used on career exploration programming as early as fifth grade. Here are four strategic actions that states can take to expand and enhance career exploration programs that prepare learners for postsecondary education and career success, based on a recent nationwide study of middle school career exploration programs, commissioned by American Student Assistance® (ASA).
Clearly define middle school career exploration and ensure a unified definition is adopted across relevant agencies and partners, including K-12, postsecondary, workforce, and relevant community-based organizations. A quality definition clearly defines middle school career exploration as a strategy that will help learners build their understanding of career interests and expand awareness and understanding of career opportunities, including through hands-on, applied experiences.
Once a clear definition is established, coordinate related and supporting efforts across state leadership, including departments driving academics and instruction, school counseling, CTE, and workforce training. Establish routines for collaboration between programmatic leaders who should be working together to support an overall vision for learner success with elements from each of their programs.
Integrate career exploration into your accountability and data collection systems. The last two years of high school are insufficient for dramatically increasing learners’ readiness for postsecondary and career opportunities. States can leverage program quality indicators in Perkins V and the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) state plans to formally set measurable goals for middle school career exploration, integrating them into existing college and career readiness (CCR) targets. States can also utilize their data collection systems to not only identify middle school career exploration participants and determine their positive placement within high school CTE programs, but also to ensure the quality of programming through evaluations or learner-based software platforms.
The report also highlights seven states that have distinguished themselves by instituting formal accountability mechanisms to influence district and school focus on meaningful career exploration. Although federal changes made through the reauthorization of ESSA allowed states to exercise flexibility in the indicators used to assess districts and schools, only two states—Pennsylvania and Georgia—have used this flexibility to include career exploration as a component in their federal accountability systems. Five additional states—Missouri, Kansas, Utah, South Carolina, and Michigan—have incorporated middle school career exploration into their state accountability mechanisms to assess the quality of delivery of career advisement services or activities.
Assess and address state policies that have the potential to limit learners’ ability to access different career exploration opportunities, including restricting CTE course enrollment by grade level or grade point average minimums.
It’s important to provide innovative and comprehensive career exploration that includes CTE. Only 33 states facilitate exploration via a course or set of courses that can serve as an on-ramp to a CTE pathway, according to ASA’s report. In contrast, the study highlights Utah’s College & Career Awareness Program, which requires a course that enables learners in grades 7-8 to explore high school, college, and career options based on individual interests, abilities, and skills. A team of CTE teachers, school counselors, and work-based learning coordinators teach the course and provide instruction in career development.
This well-rounded, effective approach equips all learners with the information they’ll need to understand their options and make informed, confident decisions about their futures.
Julie Lammers is Senior Vice President of Advocacy and Corporate Social Responsibility at American Student Assistance® (ASA), a national nonprofit changing the way kids learn about careers and prepare for their futures. Julie leads ASA’s philanthropic strategy as well as ASA’s advocacy efforts on both the federal and state level. Julie has been at ASA since March 2010.


 Over the past six months, four states,
Over the past six months, four states, 

 In March 2021, Advance CTE released
In March 2021, Advance CTE released  Once DSD administration began conversations with educators and staff, they recognized the need to create schoolwide “Without Limits Teams,” comprised of a school administrator, special education staff, school counselors, and the school’s CTE coordinator. Last spring, school staff from each of the 25 DSD schools were each brought together in full day district-wide workshops structured on the five CTE Without Limits principles and designed using Advance CTE’s
Once DSD administration began conversations with educators and staff, they recognized the need to create schoolwide “Without Limits Teams,” comprised of a school administrator, special education staff, school counselors, and the school’s CTE coordinator. Last spring, school staff from each of the 25 DSD schools were each brought together in full day district-wide workshops structured on the five CTE Without Limits principles and designed using Advance CTE’s 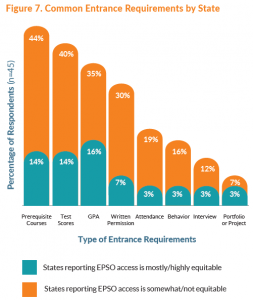 3.Identify and remove barriers to access, including restrictive costs or entrance requirements, and target specific learner populations for recruitment.
3.Identify and remove barriers to access, including restrictive costs or entrance requirements, and target specific learner populations for recruitment. 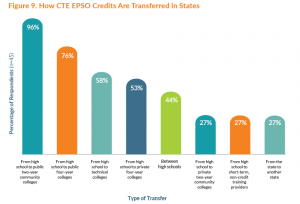 5.Expand statewide and inter-state articulation agreements to account for all types of CTE EPSOs. Statewide agreements can help guarantee recognition of CTE EPSO credit and facilitate automatic transfer between a secondary institution and a corresponding postsecondary institution of the learner’s choice. Ensuring that the transfer of credit is as frictionless as possible is vital to supporting learners as they transition into postsecondary education and continue in a degree program. As states work to ensure that each learner’s EPSO experiences consistently are counted toward articulated credit, they should also ensure that this credit contributes to core credits in a CTE program of study and not just elective credit. States can develop additional guidelines and legislation that ensures the connection between an EPSO and a program of study. Ohio has Career-Technical Assurance Guides (CTAGs) that provide automatically articulated and transferable credit upon completion of CTE coursework.
5.Expand statewide and inter-state articulation agreements to account for all types of CTE EPSOs. Statewide agreements can help guarantee recognition of CTE EPSO credit and facilitate automatic transfer between a secondary institution and a corresponding postsecondary institution of the learner’s choice. Ensuring that the transfer of credit is as frictionless as possible is vital to supporting learners as they transition into postsecondary education and continue in a degree program. As states work to ensure that each learner’s EPSO experiences consistently are counted toward articulated credit, they should also ensure that this credit contributes to core credits in a CTE program of study and not just elective credit. States can develop additional guidelines and legislation that ensures the connection between an EPSO and a program of study. Ohio has Career-Technical Assurance Guides (CTAGs) that provide automatically articulated and transferable credit upon completion of CTE coursework. In April 2021, Advance CTE released
In April 2021, Advance CTE released  With a focus on recruitment and retention, it is important for learners and families of CTE to see success stories of individuals who look like them and share similar educational, racial, socio-economic, gender and geographic backgrounds.
With a focus on recruitment and retention, it is important for learners and families of CTE to see success stories of individuals who look like them and share similar educational, racial, socio-economic, gender and geographic backgrounds. Families and learners both participating in and considering CTE highly value an education experience that allows learners to explore opportunities after high school that lead to college and career success. In this example, Utah used graphics of learners engaging in real-world skills training to promote its Auto Mechanics and Repairs career pathway. This is a way of demonstrating the connection from CTE courses, work-based learning settings and youth apprenticeship programs to career success.
Families and learners both participating in and considering CTE highly value an education experience that allows learners to explore opportunities after high school that lead to college and career success. In this example, Utah used graphics of learners engaging in real-world skills training to promote its Auto Mechanics and Repairs career pathway. This is a way of demonstrating the connection from CTE courses, work-based learning settings and youth apprenticeship programs to career success. Using local examples can help explain the nuts and bolts of how CTE delivers success by making the connection between CTE and a specific career or industry, as well as highlighting partnerships with local colleges and employers that are recognizable to parents/guardians and learners.
Using local examples can help explain the nuts and bolts of how CTE delivers success by making the connection between CTE and a specific career or industry, as well as highlighting partnerships with local colleges and employers that are recognizable to parents/guardians and learners. Wisconsin CTE showcased CTE to parents/guardians and learners by lifting up student success stories. One avenue to find compelling learner examples is to coordinate with statewide or local Career Technical Student Organizations (CTSOs) and gather testimonials, photos and stories to share on social media. This tweet focused on a local learner success story to create human interest in CTE. To help expand the reach of this tweet, Wisconsin CTE used relevant hashtags and tagged the state CTSO and the university the learner was attending. This type of post is a great way to highlight CTE and the many ways CTE benefits learners.
Wisconsin CTE showcased CTE to parents/guardians and learners by lifting up student success stories. One avenue to find compelling learner examples is to coordinate with statewide or local Career Technical Student Organizations (CTSOs) and gather testimonials, photos and stories to share on social media. This tweet focused on a local learner success story to create human interest in CTE. To help expand the reach of this tweet, Wisconsin CTE used relevant hashtags and tagged the state CTSO and the university the learner was attending. This type of post is a great way to highlight CTE and the many ways CTE benefits learners.  Developed with input from nearly 200 national, state and local education and workforce development leaders and supported by 40 national organizations,
Developed with input from nearly 200 national, state and local education and workforce development leaders and supported by 40 national organizations,  Two hallmarks of a high-quality career pathway are seamless transitions across secondary and postsecondary education and offering learners the opportunity and means to participate in early postsecondary opportunities (EPSOs) – which include dual enrollment, dual credit, concurrent enrollment and other related opportunities. It is critical that these opportunities seamlessly result in articulated postsecondary credit for learners in a degree program that will help them progress on their chosen career pathway with no hidden barriers.
Two hallmarks of a high-quality career pathway are seamless transitions across secondary and postsecondary education and offering learners the opportunity and means to participate in early postsecondary opportunities (EPSOs) – which include dual enrollment, dual credit, concurrent enrollment and other related opportunities. It is critical that these opportunities seamlessly result in articulated postsecondary credit for learners in a degree program that will help them progress on their chosen career pathway with no hidden barriers.