The Brookings Institution looks at employment outcomes for low-income learners
It’s a question that has puzzled education researchers for decades: what is the right mix of experiences in early adolescence that is most predictive of future career success and lifelong learning?
For the longest time, the rule of thumb has been “get a bachelor’s degree and you’ll get a good job.” But we know that there are other experiences on the path to a four-year degree (such as participating in work-based learning or earning an industry-recognized credential) that are just as powerful in preparing learners for their future careers. What are these experiences? And how should they be delivered to maximize learner outcomes?
New research from the Brookings Institution sheds a little bit of light on this question. The study looks at different factors that are correlated with economic success among 29-year-olds from “disadvantaged” backgrounds. The study finds that:
- Participating in work-based learning is correlated with attainment of “high-quality” jobs later in life
- Working (and earning high wages) at a young age predicts higher job quality in adulthood
- Earning credentials is still the biggest predictor of career success, but sub-baccalaureate credentials are also important
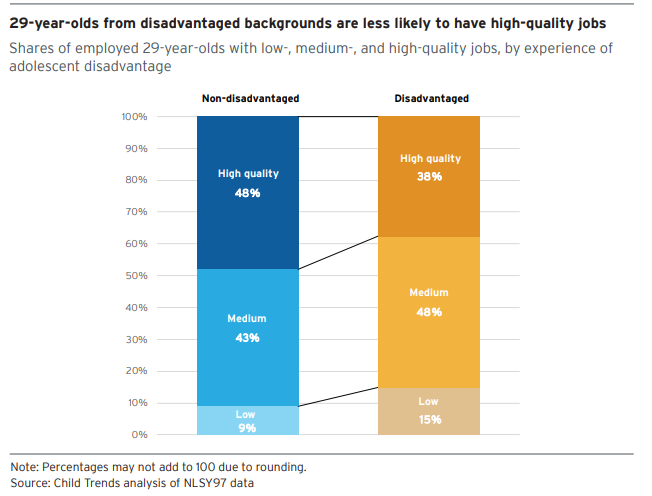 Specifically, the researchers find that participating in “relationship-focused CTE” (a term they use to refer to work-based learning and other activities where students interact with industry mentors) is significantly related to higher job quality scores at age 29. This would seem to suggest that building relationships with industry mentors and completing work-based learning at an early age can help learners, particularly low-income learners, get a leg up on their careers. While the data do not provide a full picture of the quality of work-based learning in the study, the evidence is promising.
Specifically, the researchers find that participating in “relationship-focused CTE” (a term they use to refer to work-based learning and other activities where students interact with industry mentors) is significantly related to higher job quality scores at age 29. This would seem to suggest that building relationships with industry mentors and completing work-based learning at an early age can help learners, particularly low-income learners, get a leg up on their careers. While the data do not provide a full picture of the quality of work-based learning in the study, the evidence is promising.
For the purpose of the study, the researchers define “disadvantaged adolescents” as those who, when they were between the ages of 12 and 18, had a family income equal to or less than 200 percent of the federal poverty line; did not have a parent with more than a high school education; had a mother who was a teenager when her first child was born; or whose family received public assistance. They defined job quality based on four factors: earnings, benefits, hours of work and job satisfaction.
CTE Research Roundup
- In a new research brief, MDRC summarizes findings from studies of three different career-focused learning programs: New York City’s Young Adult Internship Program (YAIP), YouthBuild and Year Up. Using a random assignment research design, the researchers find significant positive wage increases for completers of each program.
- JFF explores how the scope and length of Registered Apprenticeships can vary and poses the question: Are apprenticeships the next stackable credential?
- The NewDeal Forum Working Group, a national network of state and local leaders, published recommendations for policymakers to help the economy adapt to the future of work. The report includes recommendations for skill development and workforce training; modernizing the social safety net; and supporting entrepreneurship, innovation and access.
- Mathematica Policy Research shares an update on new partnerships and research focused on pathways to postsecondary education, including an examination of free tuition programs for adult learners, a study of the Better Careers initiative in California, and research into community college career planning through the Working Student Success Network. Keep an eye out for future research.
- A new study from JFF looks at Maine’s proficiency-based education system and finds some promising early results. According to the study, high school students who received a medium amount of exposure to proficiency-based education had significantly higher reported engagement; however, exposure to proficiency-based education was negatively correlated with SAT scores.
Austin Estes, Senior Policy Associate


