![]() Gaps in academic outcomes between learners of color and their White peers is a challenge that continues to perplex education leaders. Two new studies highlight promising practices for how states can begin to narrow racial disparities in academic outcomes and better prepare learners for the transition to postsecondary education through strong academic support and quality career and academic advising.
Gaps in academic outcomes between learners of color and their White peers is a challenge that continues to perplex education leaders. Two new studies highlight promising practices for how states can begin to narrow racial disparities in academic outcomes and better prepare learners for the transition to postsecondary education through strong academic support and quality career and academic advising.
Removing Barriers to Gateway Courses
Academic and technical proficiency are both essential for career readiness. Career Technical Education (CTE) secondary learners who pursue postsecondary education are required to demonstrate academic proficiency while completing technical coursework. However, traditional postsecondary placement models can be a barrier to learners, extending both the time and costs of completing a program of study, and ultimately serve as a deterrent for learners pursuing a postsecondary degree.
In a recent study, researchers at Florida State University examined how Florida reformed its introductory college-level course placement policies and the impact the reform had on learners of color. Prior to 2013, Florida postsecondary students scoring below college-ready on a statewide placement test were required to take at least one developmental education course. Nearly 70 percent of first-time-in-college learners were required to take these developmental education courses based on their placement test scores, with Black and Latinx learners being overrepresented compared to White learners. Learners had to pay tuition to enroll in these courses without receiving credits, and the courses did not count towards degree requirements. Furthermore, learners were required to successfully complete developmental education courses before they were allowed to enroll in for-credit gateway courses such as English and math.
After the Florida legislature passed Senate Bill 1720 (SB 1720) in 2013, learners who entered a Florida public high school in the 2003-2004 school year or later and graduated with a standard high school diploma were presumed to be college-ready, were exempt from college placement testing and developmental coursework, and could enroll directly into gateway English and math courses. The passage of SB 1720 also reformed developmental education courses overall by requiring colleges to design them in a way that better meets the needs of learners in the following ways:
- Compressing courses so that classes would meet more frequently over fewer weeks;
- Contextualizing courses so that material would be presented in an applied manner related to the learner’s intended major;
- Modularizing courses so that learners would be pre-assessed on a mastery of course standards and then allowed to complete customized modules for only the standards in which they did not demonstrate mastery; and
- Allowing learners to take developmental and college-level courses concurrently.
These reforms allowed learners who choose to enroll in developmental courses the opportunity to complete them faster, only enroll in the courses they needed, and complete their education on-time. Additionally, under SB 1720 colleges were required to reform their advising services, which increased learner awareness of developmental course options along with other academic services such as tutoring.
Comparing three cohorts of learners who had enrolled in a Florida postsecondary institution prior to SB 1720 (Fall 2011 – Fall 2013) and three cohorts of learners after SB 1720 (Fall 2014 – Fall 2016), researchers found that after the passage of SB 1720, the percentage of first-time college students enrolled in gateway math and English courses increased overall for learners; however, gains were most significant for learners of color and outpaced the growth of White enrollment by 15 percentage points.
Similarly, the percentage of learners who passed the introductory college-level courses increased across the board; however, the gains were much more pronounced for learners of color when compared to their White peers.
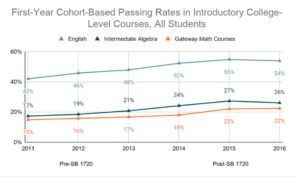
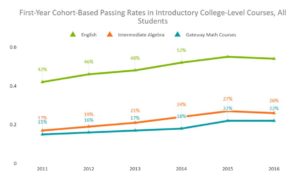
The findings from this study indicate that traditional postsecondary placement models may be underestimating the ability of learners to be successful in college-level courses, particularly learners of color who are overrepresented in developmental education.
STEM Dual Enrollment Leading to College Persistence
Another study by the Community College Research Center (CCRC) illustrates the importance of dual enrollment courses in reducing racial/ethnic gaps in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) program outcomes. About one-third of CTE high school concentrators pursue a program of study in the STEM Career ClusterⓇ, reaffirming that high-quality CTE programs can provide a strong foundation for and serve as a delivery system of STEM competencies for a broader range of learners.
CCRC found that when Florida high school learners enrolled in college-level algebra courses through dual enrollment, they were more likely to pursue and persist in STEM programs in their first year of college compared to learners who did not participate in dual enrollment. When disaggregated by race/ethnicity, the study found that, even though dual enrollment algebra learners were much more likely to be White, Black and Latinx learners who enrolled in dual enrollment courses were much more likely than White learners to enroll and persist in STEM programs in college.
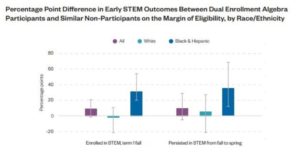
Conclusion
Taken together, these studies suggest promising practices that can narrow racial/ethnic academic achievement and opportunity gaps and prepare learners for success along their career pathway. The research demonstrates how increased access to introductory college-level courses, strong academic supports, quality career and academic advising, and access to college in high school programs can have significant access and equity implications and begin reducing disparities in outcomes for Black and Latinx learners.
For more information on advising and dual enrollment, please visit the Learning that Works Resource Center.
Brian Robinson, Policy Associate
Tags: Access and Equity, dual enrollment, Florida, STEM

