![]() Advance CTE’s “Research Round-Up” blog series features summaries of relevant research reports and studies to elevate evidence-backed Career Technical Educational (CTE) policies and practices and topics related to college and career readiness. This month’s blog highlights the benefits of skills-based hiring that closely aligns with Advance CTE’s vision for the future of CTE where statewide systems and institutions effectively support each learner to earn credentials that are counted, valued, and portable.
Advance CTE’s “Research Round-Up” blog series features summaries of relevant research reports and studies to elevate evidence-backed Career Technical Educational (CTE) policies and practices and topics related to college and career readiness. This month’s blog highlights the benefits of skills-based hiring that closely aligns with Advance CTE’s vision for the future of CTE where statewide systems and institutions effectively support each learner to earn credentials that are counted, valued, and portable.
Public sector jobs are necessary for the continued function of our society, but they are struggling to maintain staffing. The Center for American Progress’s report, The Benefits of Skills-Based Hiring for the State and Local Government Workforce, recommends that “state and local government shift to using skills-based hiring practices to expand and diversify the hiring pool and meet the sector’s skills needs.” This shift would be a departure from the present trend of state and local agencies requiring degrees that act as a proxy for skills. Skills-based hiring is gaining momentum and early implementation has shown promise. Adopting a skills-based approach for employees can be accomplished through initiatives that are already established in many states such as upskilling, teaching an employee new skills at any point in their tenure, or registered apprenticeships, a formal model that combines on-the-job training, classroom instruction and wage progression.
The Center for American Progress defines skills-based hiring as the practice of describing a job by the technical skills required to perform it. Employers use skills-based hiring practices to fill vacancies by assessing whether a candidate’s skillset aligns with those needed. This report suggests that skills-based hiring is mutually beneficial for institutions and job candidates. Removing the bachelor’s degree requirement on job listings has the potential to increase the talent pool of potential candidates for open public sector positions and position government institutions as more competitive employers.
Talent Pool Demographics
More than 70 million Americans are skilled through alternative routes (STARs), a term coined by Opportunity@Work in their report, Reach for the STARs: Realizing the Potential of America’s Hidden Talent Pool. These individuals have either a high school diploma, some college, an associate’s degree or other credentials, but they do not hold a bachelor’s degree, which is the typical educational screen employers put on job postings. This requirement acts as a barrier for workers who are skilled through alternative routes ineligible for public sector jobs.
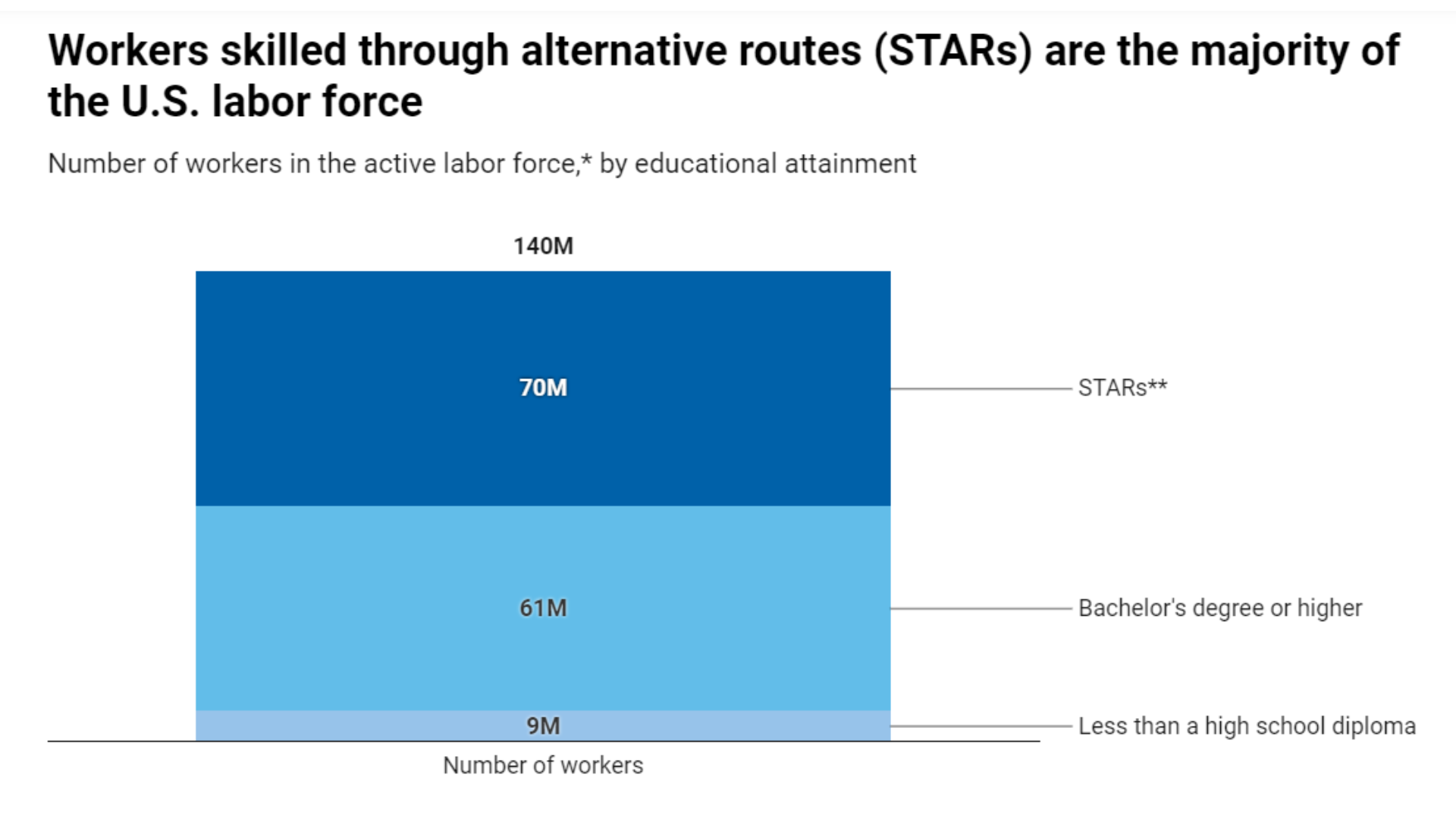
*Opportunity@Work excludes 20 million workers under age 25 from its analysis of the labor force to ensure that the majority of the population studied has completed their education. **STARs are workers who have attained a high school diploma but not a bachelor’s, master’s, or doctoral degree. Chart: Center for American Progress Source: Opportunity@Work, “Rise with the STARs,” available at https://opportunityatwork.org/our-solutions/stars-insights/rise-with-the-stars-report/ (last accessed October 2022).
By reconsidering degree requirements, public sector jobs can again be the engines of mobility they once were and reflect the demographics of the constituents they serve. The skills that STARs have built through alternative routes and pathways can be transferable from one job to another.
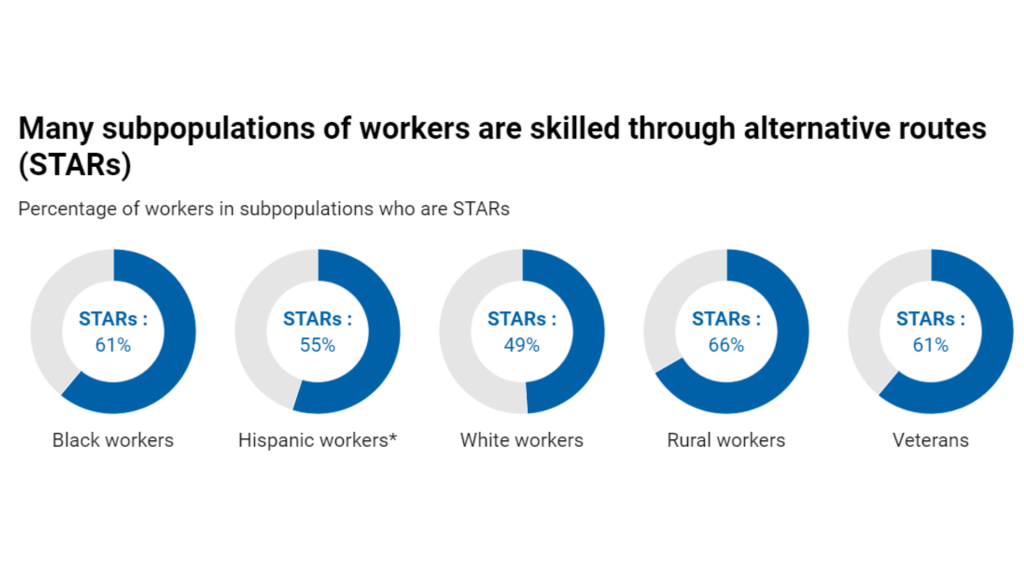
*The proportion of Hispanic workers who are STARs is lower because Hispanic workers are less likely to have obtained a high school diploma. Source: Opportunity@Work, “STARsInsights,” available at https://opportunityatwork.org/our-solutions/stars-insights/hispanic-stars/ (last accessed October 2022); Opportunity@Work calculations based on U.S. Census Bureau, “ACS 1-Year Estimates Public Use Microdata Sample: YEAR 2021 ANALYZED,” available at https://data.census.gov/mdat/#/ (last accessed October 2022).
Skills-based hiring practices can make governments more competitive employers
State and local governments are facing a significant labor shortage as their workforce comes closer to retirement. Retiring workers (currently comprising twenty-eight percent of state and local government workforce) are far less likely to have a bachelor’s degree than younger workers. This suggests that the barrier to entry to these positions has increased over time and is not mandatory for these positions.
This report recommends the following five principles to make a skills-based hiring policy successful in state and local governments:
- Involve key stakeholders.
- Identify target job roles.
- Reconsider degree requirements to build a skills-based job description.
- Build recruitment partnerships.
- Invest in worker training.
Additional resources about skills-based hiring can be found in Advance CTE’s Resource Center.
- Recording: Skills-based Hiring Webinar from April 2022
- Advance CTE’s Report: Shifting the Skills Conversation; Employer Attitudes on and Outcomes for Career and Technical Education
Amy Hodge, Policy Associate
Tags: employability skills, Equity and Access, skilled workforce, skills training, workforce data, workforce development

