 How long does it take to read through and analyze 17 state plans under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)? Two months seems to be the sweet spot for many of the nation’s education thought leaders. Since the first submission window closed this spring, a number of groups, Advance CTE among them, have released their takes on the first round of state plans.
How long does it take to read through and analyze 17 state plans under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)? Two months seems to be the sweet spot for many of the nation’s education thought leaders. Since the first submission window closed this spring, a number of groups, Advance CTE among them, have released their takes on the first round of state plans.
Federal education policy inevitably draws opinions, advice and criticism from all corners of the country, and states’ planning around ESSA implementation has been no exception. Below we round up some of the latest takes and summarize conclusions from the first round of submitted plans.
ESSA: Early Observations on State Changes to Accountability Systems (Government Accountability Office)
Purpose: The GAO was requested by Congress to study and report on states’ progress and approaches toward amending accountability under ESSA. To conduct the report, GAO policy researchers interviewed national stakeholders and met with education officials in California and Ohio, two states that were identified as taking different approaches to accountability.
Key Findings: The report finds that states are taking advantage of increased flexibility under ESSA, though the degree of change ranges by state. The authors classify ESSA accountability development by four dimensions: 1) determining long-term goals, 2) developing performance indicators, 3) differentiating schools and 4) identifying and assisting low-performers.
ESSA Equity Dashboards (Alliance for Excellent Education)
 Purpose: To highlight strengths and draw attention to growth areas in ESSA plans, the Alliance for Excellent Education is developing ESSA Equity Dashboards that rate key components of state plans. Dashboards are available for five of the first 17 plans, with the remaining expected in August. The dashboards examine long-term goals, support and intervention, and accountability.
Purpose: To highlight strengths and draw attention to growth areas in ESSA plans, the Alliance for Excellent Education is developing ESSA Equity Dashboards that rate key components of state plans. Dashboards are available for five of the first 17 plans, with the remaining expected in August. The dashboards examine long-term goals, support and intervention, and accountability.
Key Findings: The Alliance for Excellent Education highlights Louisiana’s plan for its focus on academic outcomes and the design of the state’s “Strength of Diploma Indicator.” Reviewers flagged Colorado’s long-term goals for math and reading performance.
ESSA Leverage Points: 64 Promising Practices from States for using Evidence to Improve Student Outcomes (Results for America)
Purpose: This analysis from Results for America examines the first 17 submitted ESSA plans and evaluates the degree to which states aim to use evidence-based practices in certain parts of their plan. The analysis is based on 13 key ESSA leverage points identified by Results for America and the Council of Chief State School Officers. Leverage points include monitoring local education agency implementation, allocating school improvement funds, monitoring and evaluating school improvement, and more.
Key Findings: The reviewers found that:
- Sixteen states included at least one promising practice for building and using evidence to
improve student outcomes.
- However, only four states emphasized the role of evidence-based practices through Title II and Title IV and only nine states prioritize evidence when reviewing and approving school improvement funding applications.
An Independent Review of ESSA State Plans (Bellwether Education Partners and the Collaborative for Student Success)
Purpose: To supplement the Department of Education’s peer review process, Bellwether Education Partners and the Collaborative for Student Success convened a peer review team of their own, drawing together more than 30 local, state and national experts to review and rate state plans. Their analysis focused on nine key elements.
Key Findings: The results of the peer review are broken down by state at https://checkstateplans.org/. Overall, the reviewers found that:
- States are taking advantage of increased flexibility to broaden their accountability systems, focusing on college- and career-readiness, year-to-year student growth and other indicators including science, attendance, physical education, art and school climate.
- However, many states could not describe how their proposals would play out in practice, neglecting to specify how many schools would be identified for improvement or how federal funds would be used to increase student success.
Leveraging ESSA to Promote Science and STEM Education in States (Achieve)
Purpose: This analysis from Achieve examines 17 round 1 state ESSA plans through the lens of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) education, pinpointing how states are leveraging assessments, graduation requirements and other goals to promote science and STEM.
Key Findings: Achieve’s analysis finds that, among the 17 round 1 state plans:
- Only two states set clear achievement goals around science;
- Ten states are including science in their accountability system (though many included measures under the academic achievement indicator, which has been disputed by the U.S. Department of Education); and
- Several states are exploring opportunities to use grant funds under Title II and Title IV to support STEM education.
Making the Most of ESSA: Opportunities to Advance STEM Education (Education First)
Purpose: Education First, with support from the Overdeck Family Foundation, examined 25 state plans (including 17 submitted plans and an additional eight draft plans) to identify leverage points for STEM education and review whether and how states are taking advantage of these opportunities. Their review focused on four key dimensions of state plans: inclusion of state science assessments in accountability systems; including of Career Technical Education (CTE) indicators in accountability systems; inclusion of Advanced Placement (AP) and International Baccalaureate indicators in accountability systems; and STEM elements in 21st Century Community Learning Centers.
Key Findings: The reviewers found that:
- Seventeen states included or are strongly considering including performance on state science assessments in their accountability systems;
- Seventeen states included or are strongly considering including CTE indicators in their accountability systems;
- Nineteen states included or are strongly considering including Advanced Placement/ International Baccalaureate indicators in their accountability systems; and
- Ten states are requiring or encouraging STEM activities in their 21st Century Community Learning Centers grants.
Reflections on State ESSA Plans (American Institutes for Research)
Purpose: Researchers at the American Institutes for Research reviewed 17 submitted plans and three additional draft plans to get a broad perspective on how states are prioritizing certain strategies. Their analysis covered plans for accountability, STEM, school improvement, technology and more.
Key Findings: Notably, the researchers at AIR found that, among the 20 plans reviewed:
- State accountability systems are becoming more sophisticated, including indicators such as college- and career-readiness and chronic absenteeism.
- However, states have a ways to go to more fully develop indicators of career readiness (a question recently explored at length by Education Strategy Group and the Council of Chief State School Officers).
Overall, reviewers seem impressed with states’ efforts to include more comprehensive indicators of student success in their accountability system. However, states were light on details about how their plans will be implemented and how schools will be supported to improve student performance. The remaining two-thirds of states planning to submit plans in September can draw on these findings, along with Advance CTE’s report on career readiness and ESSA, to ensure their plans are robust and sufficiently leverage all that ESSA has to offer.
Austin Estes, Policy Associate
 Similarly, in Ohio, three community colleges received state approval to offer bachelor’s degrees in microelectronic manufacturing, aviation, unmanned aerial systems, land surveying and culinary and food science. These programs still need to receive accreditation from the Higher Learning Commission before the community colleges can offer the degrees.
Similarly, in Ohio, three community colleges received state approval to offer bachelor’s degrees in microelectronic manufacturing, aviation, unmanned aerial systems, land surveying and culinary and food science. These programs still need to receive accreditation from the Higher Learning Commission before the community colleges can offer the degrees.

 Oregon’s Gov. Kate Brown launched the
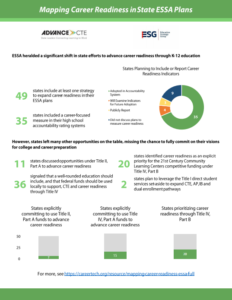
Oregon’s Gov. Kate Brown launched the  2017 was a banner year for Career Technical Education (CTE). Overall, 49 states and the District of Columbia passed a total of 241 policies related to CTE and career readiness, a marked increase from 2016. But while it is encouraging to see a groundswell of enthusiasm for CTE at the local, state and national levels, how will states leverage CTE’s momentum and ensure that state action translates to better outcomes for students?
2017 was a banner year for Career Technical Education (CTE). Overall, 49 states and the District of Columbia passed a total of 241 policies related to CTE and career readiness, a marked increase from 2016. But while it is encouraging to see a groundswell of enthusiasm for CTE at the local, state and national levels, how will states leverage CTE’s momentum and ensure that state action translates to better outcomes for students?  There was also a lot of activity related to data, reporting and accountability, largely due to state work around the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). In 2017, 35 states identified measures of career readiness in their federal accountability systems, and many of these measures included industry-recognized credential attainment, dual-credit completion and work-based learning participation.
There was also a lot of activity related to data, reporting and accountability, largely due to state work around the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). In 2017, 35 states identified measures of career readiness in their federal accountability systems, and many of these measures included industry-recognized credential attainment, dual-credit completion and work-based learning participation.
 This year marked a pivotal moment for K-12 education. With the passage of the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) in 2015, state leaders have spent the last two years reexamining and strategizing they way they deliver K-12 education. Now that the last ESSA plans have been written and submitted, we finally have a national picture of state priorities for education, including how K-12 education systems will support and reinforce career preparation opportunities.
This year marked a pivotal moment for K-12 education. With the passage of the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) in 2015, state leaders have spent the last two years reexamining and strategizing they way they deliver K-12 education. Now that the last ESSA plans have been written and submitted, we finally have a national picture of state priorities for education, including how K-12 education systems will support and reinforce career preparation opportunities.  The demand for Bachelor’s degrees may be
The demand for Bachelor’s degrees may be  In Vermont, Governor Phil Scott announced the launch of a new initiative called
In Vermont, Governor Phil Scott announced the launch of a new initiative called  Nearly two years of planning came to a head on Monday as states hit the second plan submission window under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). Under the law, states are required to engage in stakeholder consultation and develop a comprehensive, statewide strategy for spending and holding districts and schools accountable for billions of dollars in K-12 federal education funding.
Nearly two years of planning came to a head on Monday as states hit the second plan submission window under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). Under the law, states are required to engage in stakeholder consultation and develop a comprehensive, statewide strategy for spending and holding districts and schools accountable for billions of dollars in K-12 federal education funding.  Meanwhile, the Ohio Department of Education expanded options for students on the credential graduation pathway by
Meanwhile, the Ohio Department of Education expanded options for students on the credential graduation pathway by 
 How long does it take to read through and analyze 17 state plans under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)? Two months seems to be the sweet spot for many of the nation’s education thought leaders. Since the first submission window closed this spring, a number of groups,
How long does it take to read through and analyze 17 state plans under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)? Two months seems to be the sweet spot for many of the nation’s education thought leaders. Since the first submission window closed this spring, a number of groups,  Purpose:
Purpose: