Guest blog from Dr. René Cintrón, Chief Academic Affairs Officer, LCTCS
Why Credit for Prior Learning?
Credit for prior learning (CPL) – often described by the American Council on Education as academic credit granted for knowledge and skills gained outside the classroom – supports the unique mission of community and technical colleges. These colleges provide students with the opportunity to earn affordable credentials in a timely fashion that lead to valuable employment and/or transfer, whether the credential is an industry-based certification or a career-technical or transfer degree.
Unfortunately, not every student completes their program. We surveyed Louisiana community and technical college students who withdrew from courses, and found that only 18 percent gave an academic reason for doing so. By far, more students were leaving college without completing a credential because of personal (53 percent) and/or financial (31 percent) reasons. Thus, the majority of students are not withdrawing because of challenges with course content but rather – simply put – because of time and money. CPL has the ability to tackle both of these challenges for students.
Our students come to our colleges with a wealth of knowledge they obtained through their careers, past learning, military service and life experiences. When relevant, this knowledge can and should be applied to progress towards an academic credential. A few years ago, we started working with military partners in the state to increase the number of military students who enroll and graduate. Our approach was to treat the military transcript as an academic transcript. We don’t charge fees to transfer courses from other postsecondary institutions to ours, so why would we do that for students coming from the military? We took the same approach to students arriving with industry-based credentials (IBCs), transcribing and articulating these credentials as we do with courses on other transcripts. Thus, we consider these students to be “transferring in” just as students do from other institutions.
How Do We Do It?
Credit for prior learning evaluation is the process of determining how to award credit for college-level learning acquired through a variety of means. At the Louisiana Community and Technical College System (LCTCS), expert faculty groups, along with the chief academic officers’ group, met and did the work of compiling existing articulations and mapping future ones. The System reached out to entities such as the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Louisiana National Guard, the state’s Department of Education, the Louisiana Workforce Commission and the Workforce Investment Council, among others, to collect information on the various military courses and IBCs, to review them and determine which could be converted into Career Technical Education (CTE) courses.
The initial review involved each college determining its equivalent course and adding it to a matrix. The next step was to compile all of the colleges’ determinations into the system-wide articulation tables. These tables are updated and maintained on an annual basis, similar to academic catalogs. Then, importantly, the faculty and chief academic officers recognized that to ensure the staying power of their work, the process should be enacted into policy. In March 2018, the LCTCS Board of Supervisors approved revisions to Policy 1.023, which, in addition to supporting credit for prior learning, established guidelines for processing it, formalized the systemwide articulation matrix, and declared no cost to students for CPL course transcription for those in the matrix. The result: the 2018-2019 academic year, 2,073 students enrolled with credit for prior learning – a 50 percent increase from the prior year.
 This kind of collaboration and commitment across a broad scope of professionals to reward students for their prior learning efforts exemplifies how Louisiana’s community and technical colleges are supporting students in reaching their college and career goals in a timely manner.
This kind of collaboration and commitment across a broad scope of professionals to reward students for their prior learning efforts exemplifies how Louisiana’s community and technical colleges are supporting students in reaching their college and career goals in a timely manner.
For more, see Advance CTE’s report Developing Credit for Prior Learning Policies to Support Postsecondary Attainment for Every Learner


 As part of this initiative, Advance CTE has committed to developing resources to help state leaders close equity gaps in CTE. To provide state leaders with promising practices, Advance CTE added three new equity-focused policy profiles to the
As part of this initiative, Advance CTE has committed to developing resources to help state leaders close equity gaps in CTE. To provide state leaders with promising practices, Advance CTE added three new equity-focused policy profiles to the  What defines a high-quality career pathway? Is it alignment to labor market needs and career opportunities? The quality and qualifications of teachers and faculty? Access to meaningful, aligned work-based learning experiences? Perhaps all of the above?
What defines a high-quality career pathway? Is it alignment to labor market needs and career opportunities? The quality and qualifications of teachers and faculty? Access to meaningful, aligned work-based learning experiences? Perhaps all of the above?  nts at Tolsia High School in West Virginia have created an industry-validated carpentry business within their classroom. Students at Haynesville Junior/Senior High School in Louisiana are connected with physical therapists, diesel mechanics, a marriage and family counselor and other industry professionals on a biweekly basis through virtual “micro-industry engagements.” In North Dakota, nursing students can earn their associate’s degree through one of four community colleges, while taking their classes at rural hospitals and health care facilities. And in Montana, a mobile laboratory is deployed across the state to engage students around various career opportunities.
nts at Tolsia High School in West Virginia have created an industry-validated carpentry business within their classroom. Students at Haynesville Junior/Senior High School in Louisiana are connected with physical therapists, diesel mechanics, a marriage and family counselor and other industry professionals on a biweekly basis through virtual “micro-industry engagements.” In North Dakota, nursing students can earn their associate’s degree through one of four community colleges, while taking their classes at rural hospitals and health care facilities. And in Montana, a mobile laboratory is deployed across the state to engage students around various career opportunities.
 In the nine months since President Obama signed the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) into law last December, states and policymakers have been hard at work digging through the legislation and deciding how to structure their new plans. ESSA, which reauthorized the Elementary and Secondary Education Act, presents a number of opportunities to expand access to high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). As states prepare to implement the law next year, we will provide periodic updates on their progress and share strategies for leveraging ESSA to support CTE at the state level.
In the nine months since President Obama signed the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) into law last December, states and policymakers have been hard at work digging through the legislation and deciding how to structure their new plans. ESSA, which reauthorized the Elementary and Secondary Education Act, presents a number of opportunities to expand access to high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). As states prepare to implement the law next year, we will provide periodic updates on their progress and share strategies for leveraging ESSA to support CTE at the state level.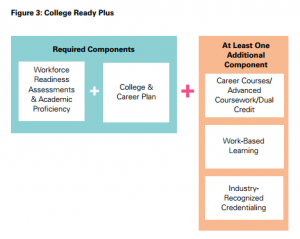 A
A 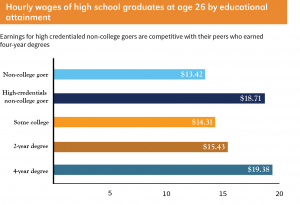 College is often considered a safe bet, but
College is often considered a safe bet, but 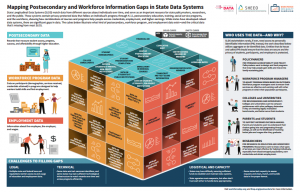 The report precedes an
The report precedes an 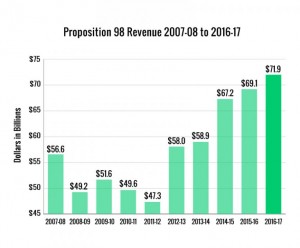 With students now on summer vacation, policymakers have been hard at work preparing for the upcoming school year – and Career Technical Education (CTE) has been front and center in several states. Last month, California approved a massive budget, including funds for the CTE Pathways Program and the new Strong Workforce Program. Meanwhile, some states are exploring strategies to address teacher shortages.
With students now on summer vacation, policymakers have been hard at work preparing for the upcoming school year – and Career Technical Education (CTE) has been front and center in several states. Last month, California approved a massive budget, including funds for the CTE Pathways Program and the new Strong Workforce Program. Meanwhile, some states are exploring strategies to address teacher shortages.