In December 2024, the Association of Career and Technical Education (ACTE) hosted its annual VISION conference in San Antonio, Texas, where Career Technical Education (CTE) administrators and practitioners gathered to network and share innovative approaches to implementing CTE nationwide. During the conference, Advance CTE and ACTE provided updates on their CTE policy-tracking efforts, highlighting 2024 CTE policy examples, trends, and popular categories.
As of December 2024, Advance CTE and ACTE have tracked 159 policies implemented across 40 states. Making a comeback as the 3rd most popular category in 2024 after falling out of the top five in 2023, Access and Equity garnered 34 policies in 2024. This resurgence demonstrates that states are increasingly prioritizing making CTE programs more accessible and equitable for all learners.
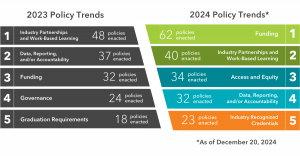
Enacted this year, the following policies reflect initiatives that make CTE more accessible and equitable specifically for underserved populations-
Idaho: Increasing Postsecondary Access to Economically Disadvantaged Learners
Idaho HB 500 established the Idaho Opportunity Scholarship to incentivize economically disadvantaged learners to complete a degree or certificate by increasing their access to postsecondary education. To qualify for this scholarship, learners must apply for federal student financial assistance and meet certain criteria to be established by the state board. The state board is required to publicize rules to determine student eligibility, academic and financial eligibility, a process for eligible students to apply, amount of awards, how eligible students will be selected when the awards shall be made, and other rules necessary for the administration of the scholarship.
Oregon: Creating Funding Mechanisms to Support Underserved Learners
Oregon S.B 1532 required the state Department of Education to create and implement a statewide plan to support “plan students,” who are defined as asylum seekers, refugees, or any other immigrants, and learners who have experienced disproportionate results in education due to historical practices. The plan must provide strategies to increase the attendance and engagement of “plan students” in educational activities. The law required the Department of Education to award grants to institutions such as early learning hubs, school districts, postsecondary institutions, tribal governments, and select community-based organizations for the implementation of the plan. Funding for these grants comes from the Department of Education Statewide Education Initiatives Account.
New Mexico: Offering Stipends to Reduce Financial Burdens for Learners
New Mexico H.B. 303 created a Workforce Training Economic Support Pilot Program to identify workforce training programs in priority industries, increase access to living-wage jobs in these industries, and increase financial stability for New Mexico residents. The three-year pilot program will offer economic support in the form of monetary stipends to cover the costs associated with basic living needs including housing, food, and transportation, and the costs associated with enrolling in and attending a workforce training program. Through the approved workforce training program identified in the pilot program, participants will acquire skills that will result in a certification, license, or credential for relevant industry employment.
 To see more policy trends and access our policy tracker, check out the Advance CTE State Policy Resources page.
To see more policy trends and access our policy tracker, check out the Advance CTE State Policy Resources page.
Velie Sando, Policy Associate


 Kristin Sine-Kinz, MBA
Kristin Sine-Kinz, MBA Dr. Stacia Smith
Dr. Stacia Smith Siva Visveswaran
Siva Visveswaran Eileen Will
Eileen Will Quindell Williams
Quindell Williams  The Launch initiative provides a large-scale platform for 14 states to not only strengthen existing career pathways systems and their impact, but to also explore innovations for reimagining pathways design and delivery for future generations of learners. Advance CTE created the Launch Collaboration Forum as a dedicated space for
The Launch initiative provides a large-scale platform for 14 states to not only strengthen existing career pathways systems and their impact, but to also explore innovations for reimagining pathways design and delivery for future generations of learners. Advance CTE created the Launch Collaboration Forum as a dedicated space for  North Carolina: Building Regional Ecosystems for Career Development
North Carolina: Building Regional Ecosystems for Career Development  Delaware: Centralizing Career Navigation Systems
Delaware: Centralizing Career Navigation Systems Vania Iscandari, senior policy associate
Vania Iscandari, senior policy associate
 Meaningful learner engagement is critical to program improvement, equity, and inclusion across CTE programs, policies, and opportunities. Leaders across Vermont are well aware of the value of leveraging learner voice in CTE. Leaders across the conference elevated existing practices and opportunities to improve programs and learning environments and meet learners’ diverse needs using their feedback, input, and leadership.
Meaningful learner engagement is critical to program improvement, equity, and inclusion across CTE programs, policies, and opportunities. Leaders across Vermont are well aware of the value of leveraging learner voice in CTE. Leaders across the conference elevated existing practices and opportunities to improve programs and learning environments and meet learners’ diverse needs using their feedback, input, and leadership.  Session 2: Achieving Inclusive CTE Goal-Setting Through Data
Session 2: Achieving Inclusive CTE Goal-Setting Through Data To learn more about Advance CTE’s resources, supports, technical assistance and/or speaking opportunities,
To learn more about Advance CTE’s resources, supports, technical assistance and/or speaking opportunities, Asantewa K. Holley
Asantewa K. Holley Dr. Kristen Klein
Dr. Kristen Klein As the Director of Constituent Services and Grant Administrator for a New York State Senator in Central New York,
As the Director of Constituent Services and Grant Administrator for a New York State Senator in Central New York,  Joe Salamone
Joe Salamone Dr. Randelle Sasa
Dr. Randelle Sasa Dana Acee
Dana Acee Boby Akhi
Boby Akhi Dr. Fiorella Cabrejos
Dr. Fiorella Cabrejos Laura Carbone
Laura Carbone Ramone Davis
Ramone Davis Hey y’all! My name is Brenna Bartlett, and I am beyond thrilled to join the Advance CTE team as the director of technical assistance. In this reimagined role, I’ll be working closely with members, states, and organizations to design and deliver tailored technical assistance that expands access to—and drives success in—high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). As a lifelong advocate for CTE, I couldn’t be more excited about the opportunity to collaborate with passionate leaders and learners from all across the country, working together to achieve even greater outcomes for our communities. Let’s get started!
Hey y’all! My name is Brenna Bartlett, and I am beyond thrilled to join the Advance CTE team as the director of technical assistance. In this reimagined role, I’ll be working closely with members, states, and organizations to design and deliver tailored technical assistance that expands access to—and drives success in—high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). As a lifelong advocate for CTE, I couldn’t be more excited about the opportunity to collaborate with passionate leaders and learners from all across the country, working together to achieve even greater outcomes for our communities. Let’s get started! A: Growing up, my family faced financial challenges, which made me acutely aware of the need for stable, well-paying jobs. For a while, I dreamt of becoming a journalist, but I quickly realized that CTE offered real, hands-on opportunities to build a sustainable career. What drew me to CTE wasn’t just financial stability; it was the chance to provide others, especially those from underserved communities, with the skills they need to succeed in today’s job market.
A: Growing up, my family faced financial challenges, which made me acutely aware of the need for stable, well-paying jobs. For a while, I dreamt of becoming a journalist, but I quickly realized that CTE offered real, hands-on opportunities to build a sustainable career. What drew me to CTE wasn’t just financial stability; it was the chance to provide others, especially those from underserved communities, with the skills they need to succeed in today’s job market.