Numerous governors have celebrated or prioritized Career Technical Education (CTE) during their annual State of the State Addresses to their state legislatures this year. When outlining their policy agendas for 2019, many governors highlighted successes related to CTE and committed to fostering CTE in their respective states.
Governors prioritized expanding access to CTE for learners. In New Hampshire, Governor Chris Sununu announced an $8.6 million allocation to remove barriers, such as tuition and transportation, to CTE participation. In Idaho, Governor Brad Little mentioned that he will focus on expanding CTE opportunities for learners. Meanwhile, in Massachusetts, Governor Charlie Barker celebrated adding 4,000 seats to the state’s vocational and technical schools. In Rhode Island, Governor Gina Raimondo noted that the state increased the number of CTE programs offered in high schools by 60 percent. Both Massachusetts and Rhode Island have prioritized increasing high-quality career pathways under the New Skills for Youth (NSFY) initiative.
During the addresses, Governors also emphasized CTE funding in their states. In Maryland, Governor Larry Hogan celebrated voters’ approval of the “casino lockbox initiative,” which will provide $4.4 million in additional funding for innovative CTE programming and other educational initiatives. In North Dakota, Governor Doug Burgum dedicated $40 million in Legacy Fund earnings for career academies.
Numerous governors also celebrated work-based learning, particularly the expansion of apprenticeships. In Montana, Governor Steve Bullock highlighted that seven out of 10 two-year colleges in the state offer apprenticeship coursework. In New Jersey, Governor Phil Murphy celebrated the creation of more than 100 new apprenticeship programs that hired more than 2,000 new apprentices. In Pennsylvania, Governor Tom Wolf noted that the state increased the number of apprenticeship programs to roughly 800.
In total, more than 20 governors have celebrated or prioritized advancing CTE in their states during their State of the State Addresses. This is Advance CTE’s second blog post on the State of the State Addresses- to view the first blog post click here. Advance CTE will continue to monitor the State of the State Addresses for their relevance to CTE.
Brianna McCain, Policy Associate


 2018 was a significant year for Career Technical Education (CTE) at the federal and state levels. On July 31, 2018, the President signed the Strengthening Career and Technical Education for the 21st Century Act (Perkins V) into law, which reauthorized the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act of 2006 (Perkins IV). The reauthorization of Perkins signaled a federal commitment to and a recognition of the promise and value of high-quality CTE. Additionally, at the state level 42 states and Washington, D.C., passed a total of 146 policy actions related to CTE and career readiness, reflecting a commitment from state leaders to advance CTE.
2018 was a significant year for Career Technical Education (CTE) at the federal and state levels. On July 31, 2018, the President signed the Strengthening Career and Technical Education for the 21st Century Act (Perkins V) into law, which reauthorized the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act of 2006 (Perkins IV). The reauthorization of Perkins signaled a federal commitment to and a recognition of the promise and value of high-quality CTE. Additionally, at the state level 42 states and Washington, D.C., passed a total of 146 policy actions related to CTE and career readiness, reflecting a commitment from state leaders to advance CTE. While roughly one hundred fewer policies were passed in 2018 than in 2017, this past year’s policies still reflect a commitment from state leaders to advance CTE. A decrease in the number of CTE policies passed compared to previous years should not be misinterpreted as an indication that CTE is not a priority for states. In fact,
While roughly one hundred fewer policies were passed in 2018 than in 2017, this past year’s policies still reflect a commitment from state leaders to advance CTE. A decrease in the number of CTE policies passed compared to previous years should not be misinterpreted as an indication that CTE is not a priority for states. In fact,  Some states have involved Career Technical Education (CTE) from the onset and others are now looking to ensure CTE is part of their overall strategy. The
Some states have involved Career Technical Education (CTE) from the onset and others are now looking to ensure CTE is part of their overall strategy. The 
 The demand for Bachelor’s degrees may be
The demand for Bachelor’s degrees may be  In Vermont, Governor Phil Scott announced the launch of a new initiative called
In Vermont, Governor Phil Scott announced the launch of a new initiative called 

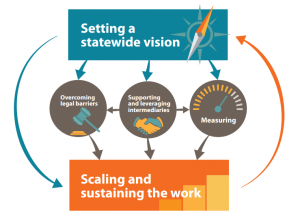 Once a statewide vision is in place and early implementation has begun, state policymakers should consider how to measure and scale work-based learning. There are two common approaches states take to building a comprehensive measurement and data-collection system: a systems-level approach that examines and evaluates the quality of the program, and a student-level approach that measures student learning and skill attainment. Through its
Once a statewide vision is in place and early implementation has begun, state policymakers should consider how to measure and scale work-based learning. There are two common approaches states take to building a comprehensive measurement and data-collection system: a systems-level approach that examines and evaluates the quality of the program, and a student-level approach that measures student learning and skill attainment. Through its