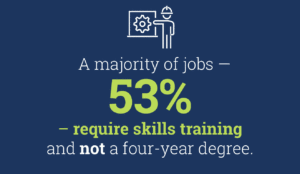
Those of us in Career Technical Education (CTE) often speak about preparing learners for careers in the real world. Well, here’s a real-world example of a sector where quite literally millions of careers are waiting to be fulfilled: construction. The number of open construction jobs averages between 300,000 and 400,000 every month. That’s an astonishing figure, especially considering how many good-paying positions await those who choose the field. Half of payroll workers in construction earn $50,460 annually, and the top 25 percent make at least $71,000.
Those of us in Career Technical Education (CTE) often speak about preparing learners for careers in the real world. Well, here’s a real-world example of a sector where quite literally millions of careers are waiting to be fulfilled: construction. The number of open construction jobs averages between 300,000 and 400,000 every month. That’s an astonishing figure, especially considering how many good-paying positions await those who choose the field. Half of payroll workers in construction earn $50,460 annually, and the top 25 percent make at least $71,000.
In the construction industry’s home building sector, employers in every state are paying top dollar for well-trained, entry-level workers. That is, if they can find any. One place they’re successfully identifying them is in high schools, community colleges and other institutions using a curriculum from the trade training nonprofit Home Builders Institute (HBI) called Pre-Apprentice Certificate Training (PACT).
HBI’s PACT curriculum is designed to provide learners with essential skills vital for careers in construction. Upon completion, graduates receive a certification in up to nine construction trade specialties. The certification is recognized and validated by the nation’s building industry. PACT, which is hands-on, competency-based curriculum, is one of only three, national curriculums approved by the U.S. Department of Labor and several state departments of education.
Gage Trebilcock, left, 17, a senior at Stonington High School, explains his technical drawing in the Pipeline in Manufacturing class he’s enrolled in to Connecticut Gov. Ned Lamont, second from left, Monday, Oct. 3, 2024. Trebilcock is enrolled in the new pilot program with the Home Builders Institute of Washington, D.C., titled the Pre-Apprenticeship Certificate Training (PACT) program. The pilot program, only the second in the state, is designed to highlight how a local public school system can promote the construction trades. | Tim Martin, The Westerly Sun
Home builders are looking for smart, hard-working and ambitious team members. States are elevating CTE’s impact by helping to support the tools and services that train new workers. HBI’s PACT is part of broad efforts by many states to create regional training opportunities, adopt skills-based hiring practices and increase equity and job quality by promoting private sector employment opportunities for a diverse workforce.
For example, in Rhode Island, the Residential Construction Workforce Partnership serves employers and educators in the state by recruiting and training people who want to join the industry as well as those seeking to upskill current employees. Since its inception, the group has used HBI’s PACT curriculum to great success.
State CTE leaders and economic development professionals understand the synergy between skills training, good jobs and economic strength. After all, wages in construction are higher than in other industries. The average hourly earnings in construction is approaching the $36 mark (in manufacturing, it’s $31.80. Transportation and utilities: $27.67. Overall, in the private sector: $33.20). That kind of solid personal income helps support the bottom line of any tax base.
More broadly, the shortage of affordable rental and for-sale homes is a challenge for every state. The U.S. faces a shortfall of 1.5 million homes, which as a matter of supply and demand, forces rents and house prices higher nationwide. Economists and housing professionals cite the skilled labor gap as a major contributor to the scarcity of affordable homes.
It’s simple. For those we together serve, gaining a valuable skill in residential construction promises limitless career opportunities. And supporting skills training makes economic sense for every state in the nation.
Learn more about PACT Curriculum and Certification: PACT One Pager
To explore how PACT can be integrated into a state’s CTE initiatives, visit HBI.org and email Partnerships@hbi.org.
Ed Brady, President and CEO, Home Builders Institute (HBI)



 As part of ongoing blog topics providing updates on this initiative, Deshaun Mars, Vice President, Global Philanthropy (Job Skills,) and Brice Thomas, Policy Associate engaged in a discussion to highlight JPMC’s view of the initiative and how this work advances JPMC’s philanthropic portfolio and ultimately building high-quality local and state career pathway systems.
As part of ongoing blog topics providing updates on this initiative, Deshaun Mars, Vice President, Global Philanthropy (Job Skills,) and Brice Thomas, Policy Associate engaged in a discussion to highlight JPMC’s view of the initiative and how this work advances JPMC’s philanthropic portfolio and ultimately building high-quality local and state career pathway systems. 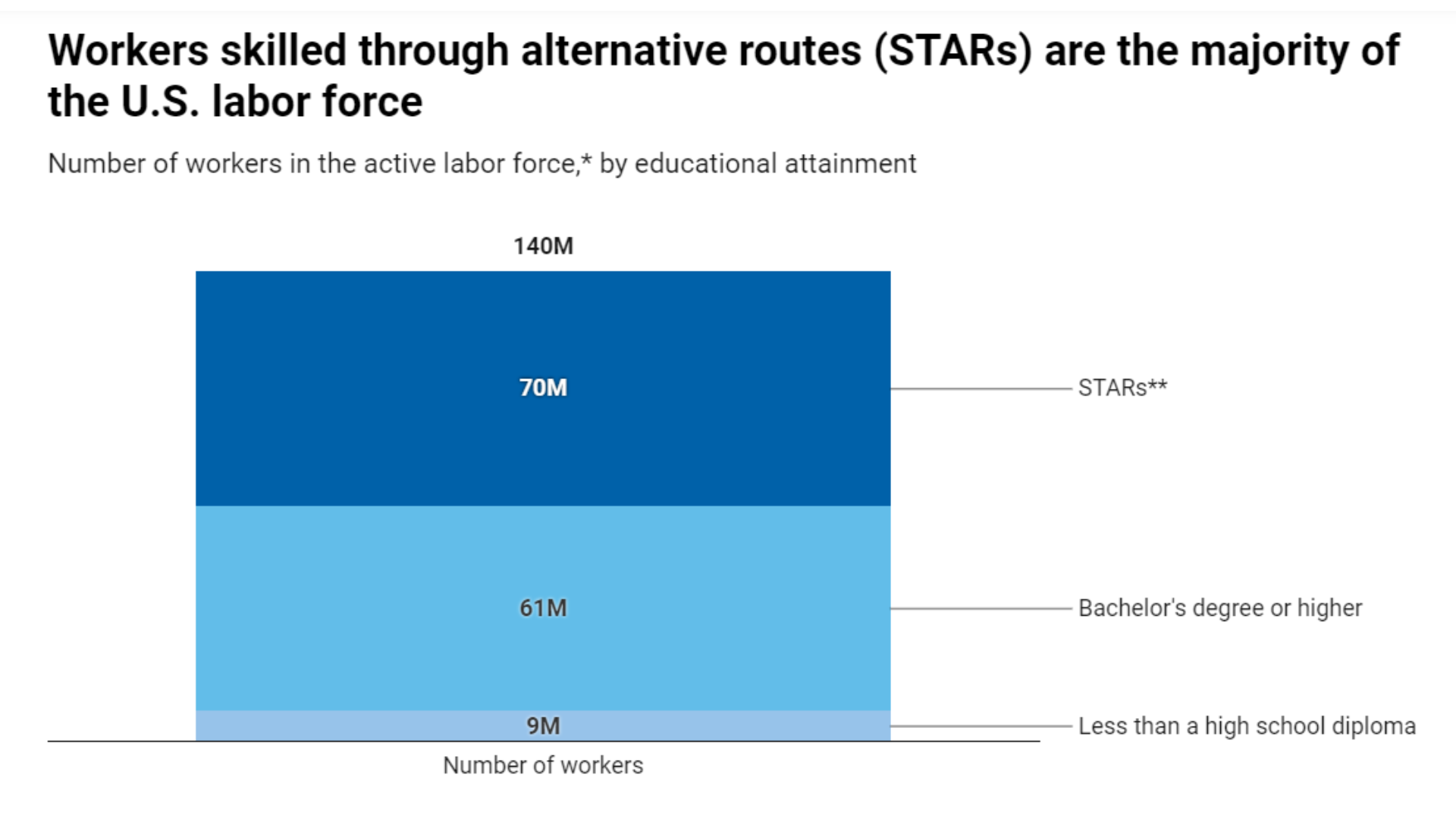
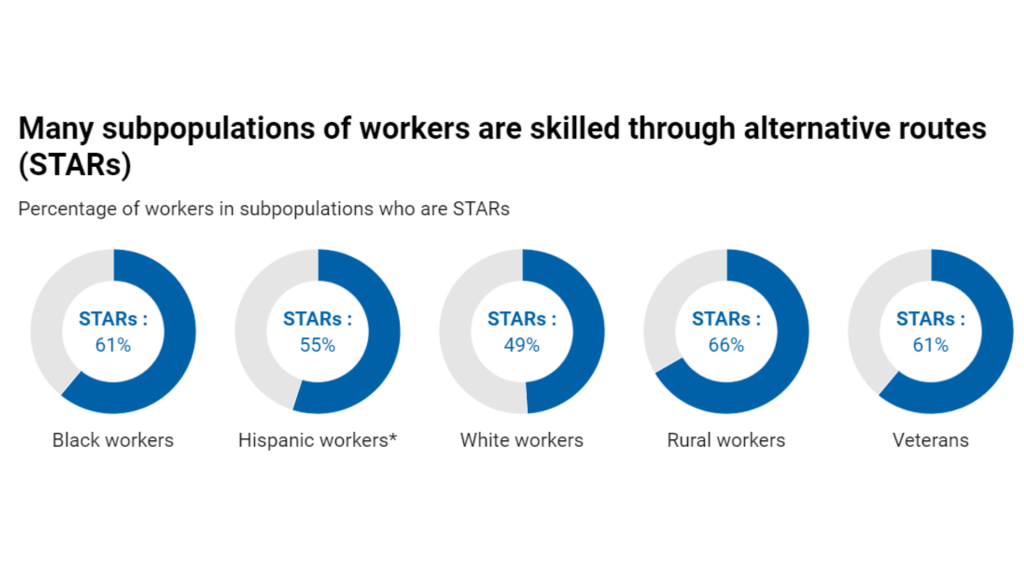
 The CCRC research points out that noncredit programs are also increasing in popularity,
The CCRC research points out that noncredit programs are also increasing in popularity,