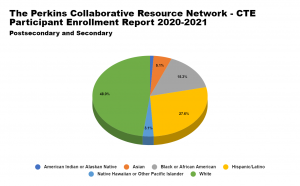
In September 2022, Advance CTE and ECMC Foundation announced the second cohort of The Postsecondary State Career Technical Education (CTE) Leaders Fellowship at Advance CTE—Sponsored by ECMC Foundation. The Advance CTE — ECMCF Fellows include representation across multiple demographic categories reflecting the Fellowship’s goal of intentionally building a postsecondary leadership pipeline for underserved populations in Career Technical Education (CTE) that closes racial representation gaps and removes equity barriers to postsecondary leadership advancement. For this next blog in the ECMCF Fellow Feature series, we interviewed ECMCF Fellow Dominique Footes (MD) who is passionate about elevating CTE and using data to advance equity for every learner.
 Tell me more about your journey to the Fellowship.
Tell me more about your journey to the Fellowship.
I was drawn to the Fellowship’s focus on using data as a tool to advocate for equity, and I had previously worked with Dr. Kevin Johnson through the Association of Career and Technical Education’s (ACTE) Inclusion, Access, Equity and Diversity Mentorship program, so I was confident that the professional development through this experience would be rigorous. He’s the type of mentor that will encourage and push you to analyze DEI issues on a deeper level and asks questions that you’ve never considered before. I knew that I was up to the challenge, and I knew that this would be an incredible opportunity for growth.
What are the skills or areas where you’ve experienced the most growth in the program?
I’ve noticed a change in my confidence and the way that I communicate. Fellowships can be intimidating, from the expert speakers to the caliber of my fellow cohort members and having the confidence to navigate these spaces is a huge success. I know that my experience as a practitioner is valuable, and now I have more confidence to ask questions to translate what might be happening in another state to apply it to our own context in Maryland. Engaging with speakers has been the highlight of this experience for me.
Engaging with other Fellows has been great. I’ve been able to learn more about how others have leveraged DEI in their work and applied similar approaches to conversations I am having with my organization’s leadership. My program is centered around career development for minority students and I’ve had the confidence to pose challenging questions that they’ve been very receptive to.
Have you been tapped for new or more advanced roles within your organization as a result of your experience in the Fellowship?
The topics we’ve explored in the Fellowship are timely with my current projects as a Special Programs Administrator. We’re looking to engage more minorities in STEM spaces and have the knowledge of how to approach this work with fidelity.
I have a lot of experience working with students. When I combine this experience with the postsecondary knowledge that I’m gaining through the Fellowship, I’ve seen that my colleagues are more willing to listen to the needs of students to support their career development experiences. I am able to speak directly about the process for re-engaging them post-COVID and what we need to do to equip them to return to the classroom.
How has your experience in the fellowship helped you explore new spaces or positions in postsecondary state CTE leadership?
My conversations and relationship with my mentor have been really valuable in helping me realize the professional opportunities that exist to support postsecondary work. Initially, I wasn’t sure of the direction I wanted to go in, but learning more about organizations that do work externally to support postsecondary programs and elevate their work with students has been really rewarding.
I’m grateful for this thought partnership, and I’ve been able to reflect on how I can continue to build a strong foundation to do meaningful work.
I feel like we’ve reached a point where we have to start looking at CTE as a starting point rather than a stop. This is a huge part of the work that I’m doing and I want to ensure that I am highlighting these programs for students so that they understand that they can access them wherever they are in their journey.
Academic exploration needs to go hand-in-hand with skills training and we need to consider how we’re reflecting this in the marketing of these programs. This work is done through advocacy and increasing awareness of what CTE is. For example, students may not understand that STEM programs fall under CTE. They need to know about all the different pathways and the spectrum within these programs for upskilling.
Tell us more about your Real-World Project which focuses on using data to provide more supportive programming for women entering STEM industry programs.
I know that engaging women in these spaces is really important and there is definitely a need to increase the number of young women in STEM programs. This issue became more urgent after the pandemic because of the disproportionate burden that was placed on women. There is acknowledgment across the STEM field and a desire to see women succeed but we need to understand the best way to support them.
My project evaluates the tools that we’re providing learners to understand the impact on their persistence in and completion of their programs. We also want to understand how they’re being prepared to transition into the workforce. I saw an opportunity to leverage and organize the data we’ve collected on women participating in CTE. I am developing a tool that aggregates the available data to develop a program that targets the specific challenges women in STEM programs are encountering.
Making sure the student is self-sufficient when they leave us and have the necessary language and tools to succeed in these industries and hopefully turn around and uplift that next group is important.
If you have any questions, contact Dominique Footes by email at dominiquefootes@gmail.com
Amy Hodge, Policy Associate


 Tell us about your journey to the Fellowship.
Tell us about your journey to the Fellowship. Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania Texas
Texas Ohio
Ohio
 Earlier this year, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce Foundation hosted a webinar to release their new report,
Earlier this year, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce Foundation hosted a webinar to release their new report,