Congress is back in session, and chatter on Capitol Hill returns to reauthorization of the Carl D. Perkins Act (Perkins), with a chamber-wide vote on comprehensive reauthorization legislation scheduled for tomorrow in the House. The bill, H.R. 5587, would reauthorize Perkins for six years and make a number of changes within the existing structure of the law, encouraging alignment with other federal legislation and streamlining the law’s requirements. You can read our analysis of the bill here.
Before lawmakers in the House vote on H.R. 5587, it is worth revisiting statements of support from members of the education, workforce development and business communities. By and large, there is cross-sector, bipartisan support for Perkins reauthorization. Yet as the 114th Congress heads into its final months, many organizations – Advance CTE included – have urged Congress to complete their work on Perkins this year. Here is a sample of statements of support from a cross-section of organizations and businesses, primarily related to the House Perkins bill as well as the reauthorization effort more generally.
Words of Support from the Education Community
“The Strengthening Career and Technical Education for the 21st Century Act builds on current law by emphasizing the importance of CTE programs of study, while maintaining the flexibility of states and local recipients to develop and implement program models that best suit their needs and available resources.†– Advance CTE and the Association for Career and Technical Education
“As states work to align education programs with current workforce needs, this legislation to update the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act will provide critical supports to state and local educators preparing students to succeed in 21st century careers.†– Council of Chief State School Officers
“H.R. 5587 reflects many of our recommendations for reauthorization. It incorporates a commitment to meaningful professional development for educators, encourages supportive partnerships that link school districts and teachers with industry partners, and promotes industry-recognized credentials and certificates for specific occupational areas.†– American Federation of Teachers
“There is much to like in the Strengthening Career and Technical Education for the 21st Act… The House bill addresses the paperwork burden by allowing districts to fill out a simple, easy-to-complete local application.†– AASA, The School Superintendents Association
“We are pleased that H.R. 5587 [supports programs closely aligned with the needs of business and industry] by encouraging states and local recipients to better coordinate activities supported by the Perkins Act with the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA) and by requiring needs assessments to guide the expenditure of Perkins funding at the local level.†– American Association of Community Colleges and Association of Community College Trustees
“H.R. 5587 recognizes and includes educators in CTE planning and decision-making. This approach strengthens collaboration among the education, business, labor, employment, and economic sectors; improves program effectiveness; and helps ensure that the needs of both students and employers are met.†– National Education Association
Business and Industry Leaders Weigh in on Perkins Reauthorization
“H.R. 5587 would be an improvement over current law. In particular, the Chamber supports the provisions of this bill that would … authorize innovation grants to improve CTE and align workforce skills with labor market needs … integrate industry-recognized credentials; and increase support for work-based learning activities through innovation grants and state leadership activities.†– The U.S. Chamber of Commerce
“There is no issue more connected to U.S. competitiveness than equipping our nation’s youth with the academic and workplace skills needed for 21st century jobs. By updating and reauthorizing the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act, Congress has an opportunity to ensure our students achieve strong academic and career preparation in the nation’s fastest growing industries.†– IBM
“We know more can be done to help educational institutions better prepare young people for today’s jobs. A modernized career and technical education (CTE) system, designed with input from employers and responsive to the needs identified by labor market data, is central to accomplishing that test.†– Toyota
“By reauthorizing the Perkins Act and reinforcing CTE programs, educators and their partners in the business community can improve student outcomes and provide the skills required to be successful in the workforce … We urge the House to swiftly pass H.R. 5587 and for the Senate to consider companion legislation in the near future with the goal of sending a Perkins Act reauthorization bill to the president’s desk in 2016.†– Associated Equipment Distributors
“[H.R. 5587] would provide agriculture education programs the funding assistance needed to create a well-rounded practical approach to learning through classroom education.†– American Farm Bureau Federation
“Among the provisions we believe will be particularly effective in driving improvements in career education: the incentives for CTE programs to incorporate work-based learning and recognition of the value of industry-driven occupational certifications. Both work-based learning and industry credentials are indispensable elements of effective career and technical education.†– Opportunity America
Workforce Development Organizations Consider the Value of New Bill
“The bill makes substantial improvements in the federal CTE law: encouraging the development of high quality programs of study; emphasizing the importance of work-based learning; encouraging the expansion of dual enrollment, concurrent enrollment, and early college high school opportunities; requiring that CTE programs are aligned with the skill needs of employers in in-demand industries and occupations; and better aligning CTE with innovations and programming established in the newly implemented Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA).†– Jobs for the Future
Op-Eds on Perkins
“The revised Perkins bill now must pass the full House and Senate. Passage of the legislation will be critical to the future of American education and our economic competitiveness. We are hopeful that the House committee’s unanimous, bipartisan approval signals that Republicans and Democrats, supported by business and labor, educators, community leaders, parents and students who are united behind common-sense solutions will result in an update of our education system, leading to a stronger economy and more opportunities for our young people.†– Stanley Litow
“The proposed reauthorization will strengthen connections between CTE programs and business and industry. Doing so will help more precisely identify the career fields, along with the skills and credentials, needed regionally.†– Mark MacCarthy
“If passed, the new Perkins Act would be a small but important step toward making sure that students get on the pathway to prosperity that’s right for them.†– Charles Sahm
“[H.R. 5587] stressed educational partnerships that align secondary and postsecondary institutions, employers, and career and technical education programs to meet local and regional labor needs now and in the future, meaning students can pursue a career path equipped with the knowledge of where job opportunities exist in their local community.†– Jim Postl
Austin Estes, Policy Associate
 America went to the polls on Tuesday and, in what was a surprise turn of events for many, Donald Trump won the race for President of the United States. The Senate, which many were closely watching to see if it would flip towards Democratic control, will retain a slim (51 votes) GOP majority. Republicans also defended their majority in the House of Representatives, retaining 239 seats in total (218 are needed for control of the chamber). Senator Tim Kaine (D-VA), the Democratic Vice Presidential candidate, is expected to return to the Senate and continue on in his current role as co-chair of the Senate CTE Caucus.
America went to the polls on Tuesday and, in what was a surprise turn of events for many, Donald Trump won the race for President of the United States. The Senate, which many were closely watching to see if it would flip towards Democratic control, will retain a slim (51 votes) GOP majority. Republicans also defended their majority in the House of Representatives, retaining 239 seats in total (218 are needed for control of the chamber). Senator Tim Kaine (D-VA), the Democratic Vice Presidential candidate, is expected to return to the Senate and continue on in his current role as co-chair of the Senate CTE Caucus.


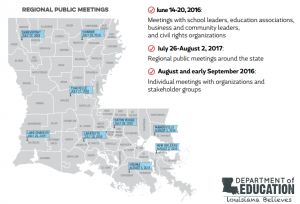 In the nine months since President Obama signed the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) into law last December, states and policymakers have been hard at work digging through the legislation and deciding how to structure their new plans. ESSA, which reauthorized the Elementary and Secondary Education Act, presents a number of opportunities to expand access to high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). As states prepare to implement the law next year, we will provide periodic updates on their progress and share strategies for leveraging ESSA to support CTE at the state level.
In the nine months since President Obama signed the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) into law last December, states and policymakers have been hard at work digging through the legislation and deciding how to structure their new plans. ESSA, which reauthorized the Elementary and Secondary Education Act, presents a number of opportunities to expand access to high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). As states prepare to implement the law next year, we will provide periodic updates on their progress and share strategies for leveraging ESSA to support CTE at the state level.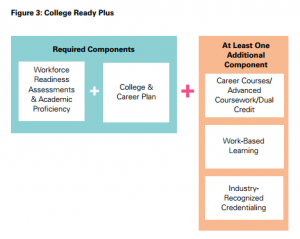 A
A 
 Work-based learning provides a continuum of activities — from career exploration and job shadowing to internships and apprenticeships — that help students develop technical and professional skills in an authentic work environment. While many work-based learning programs are designed and operated at the local level, several states have begun building a data collection and evaluation strategy to ensure program quality, identify and scale successful programs, and share promising practices. To support state efforts in this work, Advance CTE today released a brief that explores strategies for measuring work-based learning.
Work-based learning provides a continuum of activities — from career exploration and job shadowing to internships and apprenticeships — that help students develop technical and professional skills in an authentic work environment. While many work-based learning programs are designed and operated at the local level, several states have begun building a data collection and evaluation strategy to ensure program quality, identify and scale successful programs, and share promising practices. To support state efforts in this work, Advance CTE today released a brief that explores strategies for measuring work-based learning. Last month Governor Bruce Rauner of Illinois
Last month Governor Bruce Rauner of Illinois  In the postsecondary world there is
In the postsecondary world there is 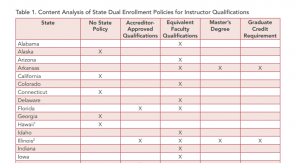 Many states allow students to earn credits in high school that can be applied towards a postsecondary degree or credential — a strategy known as dual, or concurrent, enrollment. While dual enrollment makes it easier and more affordable to obtain a postsecondary credential, states must pass policies to ensure students are receiving this advanced instruction from qualified teachers.
Many states allow students to earn credits in high school that can be applied towards a postsecondary degree or credential — a strategy known as dual, or concurrent, enrollment. While dual enrollment makes it easier and more affordable to obtain a postsecondary credential, states must pass policies to ensure students are receiving this advanced instruction from qualified teachers.