This research review series features interviews with three CTE researchers— Julie Edmunds, Shaun Dougherty, and Rachel Rosen — to highlight new and relevant Career Technical Education (CTE) research topics being pursued and discuss how state CTE leaders might leverage these to make evidence-based decisions. This series is conducted in partnership with the Career and Technical Education Research Network, which provide CTE impact studies intending to strengthen the capacity of the field to conduct and use rigorous CTE research.
This research review series features interviews with three CTE researchers— Julie Edmunds, Shaun Dougherty, and Rachel Rosen — to highlight new and relevant Career Technical Education (CTE) research topics being pursued and discuss how state CTE leaders might leverage these to make evidence-based decisions. This series is conducted in partnership with the Career and Technical Education Research Network, which provide CTE impact studies intending to strengthen the capacity of the field to conduct and use rigorous CTE research.
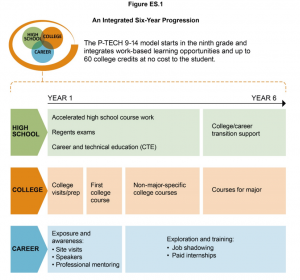
For the second post in this series, Advance CTE spoke with MDRC’s Rachel Rosen about the findings from her studies, Bridging of the School-to-Work Divide and the On-Ramp to College. These studies explore the impact that participation in New York City (NYC) P-TECH model schools has on improvement in learner outcomes for New York’s student’s college and career readiness. The NYC P-TECH Grades 9-14 (P-TECH 9-14) high school model involves a partnership among the New York City Department of Education, the City University of New York (CUNY), and employers collaborate with the schools implementing it. The schools prepare students for both college and careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields by allowing them to earn an applied associate degree in addition to a high school diploma and gain relevant work-based learning experiences within a six-year timeframe.
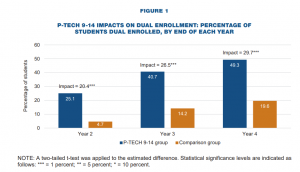
These studies compared the impact that attending one of NYC’s P-TECH had on the number of dual enrollment credits learners earned, and the passage rate of the state readiness Regents exam as college and career readiness metrics. Comparison groups of students for this study were created naturally through New York’s lottery admission system. Researchers were able to observe the outcomes of those who were admitted to a P-TECH and those who were offered seats in other schools. By the end of two years of high school, 42 percent of P-TECH 9-14 students had passed the English Language Arts exam compared to 25 percent of a comparison group of students enrolled in other high schools. There was also a positive impact on passing the regents math exam with 43 percent of P-TECH students passing it by the end of two years, compared with 40 percent of comparison group students.
Based on these findings, policymakers may be interested in learning more about how to leverage the P-TECH model to replicate positive outcomes for learner populations most underserved by traditional school models.
How do your research findings on the P-TECH school model advance the CTE field’s understanding of ways to better serve learners?
One of the important things about the P-TECH study is that it is a causal study, so we can confidently say that the results we are seeing are directly caused by students being enrolled in the P-TECH model as compared to an alternative model. The P-TECH model was developed from proven elements of other models that are also backed by rigorous evidence. These elements include early college high school models, career academies, and small schools of choice. P-TECH is a tightly aligned model where there is good coordination between secondary, postsecondary, and employers that provide a lot of cushioning for students at these critical transition points where, in other models, they might be left to their own devices.
 What findings from the Bridging of the School-to-Work Divide and the On-Ramp to College studies, would you highlight for state CTE leaders in particular?
What findings from the Bridging of the School-to-Work Divide and the On-Ramp to College studies, would you highlight for state CTE leaders in particular?
We believe that CTE leaders will be really interested in the positive impact that we’re seeing for students who are participating in P-TECH: P-TECH 9-14 students signed up for dual enrollment programs at higher rates and both attempted and earned more college credits than the comparison group students by the end of four years of high school. It is important to note that the students in the study sample intentionally had weaker academic performance in eighth grade than the overall student population enrolled in P-TECH 9-14 schools (more than 70% of them were testing below proficient in both math and English Language Arts (ELA) in 8th grade). Another important demographic piece for leaders to consider is the impact that attending a P-TECH high school has for learners traditionally underserved by comprehensive high schools. Our sample reflects learners who identify as Black and Hispanic, and who come from neighborhoods where the median income is below the city average, and they are experiencing positive outcomes with dual enrollment and passing the Regents exam.
Focusing on Bridging of the School-to-Work Divide, which indicates that the P-TECH model has positive impacts on students’ college and career readiness, what do you know about how specific elements of P-TECH contribute to this impact?
There are a couple of elements of the P-TECH model that we think contribute to student success and readiness for work-based learning and dual enrollment courses:
- First, P-TECH high schools tend to front-load the required high school classes. This means that students have more room in their schedules to fit in these college coursework-level classes when they become upperclassmen (11th and 12th grade). This is an intentional piece of the model’s design, and to make sure that students are eligible, the high schools encourage them to take their math and English Regents early. Passing the Regents* is a prerequisite to dual enrolling in CUNY classes, and students can start taking the exams as early as ninth grade.
- Second, P-TECH schools also have an explicit focus on helping students develop soft skills that prepare them for college and careers. These include skills such as teamwork and time management. Including these skills as part of the scope and sequence of the high school curriculum gives students a leg up when it comes to preparedness for their work-based learning opportunities.
- Finally, a lot of schools operate summer bridge programs to work with students who are behind and need to build up their skills. This means that they can get up to speed faster when they enter 9th grade.
Taken together, all of these elements position students for success not only in high school but in their work-based learning experiences and to dual enroll in college courses.
*The Regents Examinations are New York’s statewide standardized examinations that students take to demonstrate proficiency in core high school subjects. Students are required to pass these exams to earn a Regents Diploma.
Based on the findings in both studies, your team found that P-TECH students tended to concentrate more on CTE courses than control groups, either through accumulating greater numbers of CTE credits in high school or by taking CTE-aligned courses through dual enrollment.
What factors appear to drive that trend? And are there any implications here for CTE leaders and educators?
Yes, the P-TECH model has an explicit focus on preparing students for careers through CTE classes. The schools were set up to make these CTE classes available in high school and CTE courses were also offered at the colleges as part of the applied associate’s degrees that students can earn.
The comparison group in this study is made up of students who applied to P-TECH, but who did not win a seat through the random admissions process. Some of those students may have ended up in other high schools across New York City that also offer CTE coursework if that was important to them. However, we’re still seeing that P-TECH students earned more CTE credits than that comparison group students, and we believe that it is due to the very tight focus on CTE in these schools.
CTE leaders should certainly consider the role that industry partners have in helping to ensure alignment across the courses students take, the associate degree coursework, and standards for the industries they represent. The industry partners had some input into which CTE classes would help students be more prepared to secure jobs within the industry, or at least if not with the industry partner itself, then the industry that the partner works in. There is a lot of communication about how to best prepare students for entering these industries.
On-Ramp to College digs into the differences in dual enrollment participation based on gender, revealing that female students enroll in college courses at higher rates than males.
Can you explain what you learned about this pattern and any insights you gained about supporting male students’ college enrollment?
There is an interesting paradox that is frequently observed across the higher education and CTE literature where, despite being more likely to enroll and graduate than their male peers, female students experience lower levels of accrued impact from participating in CTE.
Since the P-TECH model has a combined focus on both higher education and career readiness, we wanted to see how the gender differences might play out for students in this environment. Consistently, we saw female students in both the P-TECH high schools and the comparison schools were much more likely to dual enroll than male students. This was not, however, translate into higher pass rates of the Regents exam. While male and female students were passing the Regents at similar levels, the female students were more likely to take up the opportunity for dual enrollment than their male peers. And this pattern was held across all seven of the P-TECH schools in this study, so it seems unrelated to the program type.
In our sample, about 21 percent of students have special education designations, but within that group, almost 80 percent of these students are male. When we compared this to the general education population, we found that the male-female gap closed somewhat, but not completely. From a policy standpoint, this tells us that there is more that could be done to support students who have special education designations in dual enrollment.
Finally, what new questions has this work raised for you that could be applied to future research?
The study is still ongoing and we are currently working on our final analysis. Generally speaking, the big open question is focused on the impacts of P-TECH on postsecondary attainment.
Other questions we’d like to explore include:
- What are the labor market outcomes for these students? We would like to be able to follow students for a longer period to see if they are more likely to get jobs or higher levels of earnings.
- P-TECH models have proliferated rapidly, both across the country and internationally, but we want to know how replicable these findings are. In New York, students are able to access the rich labor market through the city’s expansive transportation system. This makes it a lot easier for them to attend classes on different campuses and their work-based learning positions. Transportation is often a huge barrier for students to take advantage of these opportunities, so we need to find a way to disentangle this factor to better understand P-TECH’s impact.
- What does it mean to be college-ready in places that don’t have easy markers of college readiness? Finding a way to define and understand what it means to be college-ready is an important policy question.
The work of the CTE Research Network Lead is supported by the Institute of Education Sciences at the U.S. Department of Education with funds provided under the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act through Grant R305N180005 to the American Institutes for Research (AIR). The work of the Network member projects is supported by the Institute. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent the views of the Institute or the U.S. Department of Education.
Visit the Learning that Works Resource Center for additional publications examining career-centered education models and Advance CTE’s 50-state report on equity in CTE early postsecondary opportunities (EPSOs) released earlier this year.
Amy Hodge, Policy Associate
 House Lawmakers Advance FY23 Education Funding Bill
House Lawmakers Advance FY23 Education Funding Bill

 Today, Advance CTE and Education Strategy Group (ESG) released an annual report and site snapshots for year two of the
Today, Advance CTE and Education Strategy Group (ESG) released an annual report and site snapshots for year two of the 
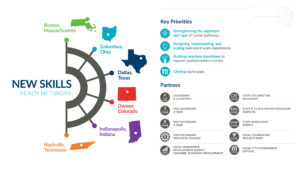
 Boston, Massachusetts,
Boston, Massachusetts,  What findings from the Bridging of the School-to-Work Divide and the On-Ramp to College studies, would you highlight for state CTE leaders in particular
What findings from the Bridging of the School-to-Work Divide and the On-Ramp to College studies, would you highlight for state CTE leaders in particular
 “Go forth without limits!” was an apt parting chat message as over 70 state Career Technical Education (CTE) leaders from across 16 states convened virtually last month to launch the community of practice for
“Go forth without limits!” was an apt parting chat message as over 70 state Career Technical Education (CTE) leaders from across 16 states convened virtually last month to launch the community of practice for  Vargas challenged attendees to dream big and be the new models for scalable solutions by being a “network facilitator,” by combining career pathway expansion with intentional investments in collaboration and sustained partnershi
Vargas challenged attendees to dream big and be the new models for scalable solutions by being a “network facilitator,” by combining career pathway expansion with intentional investments in collaboration and sustained partnershi In support of this effort, Advance CTE recently published
In support of this effort, Advance CTE recently published 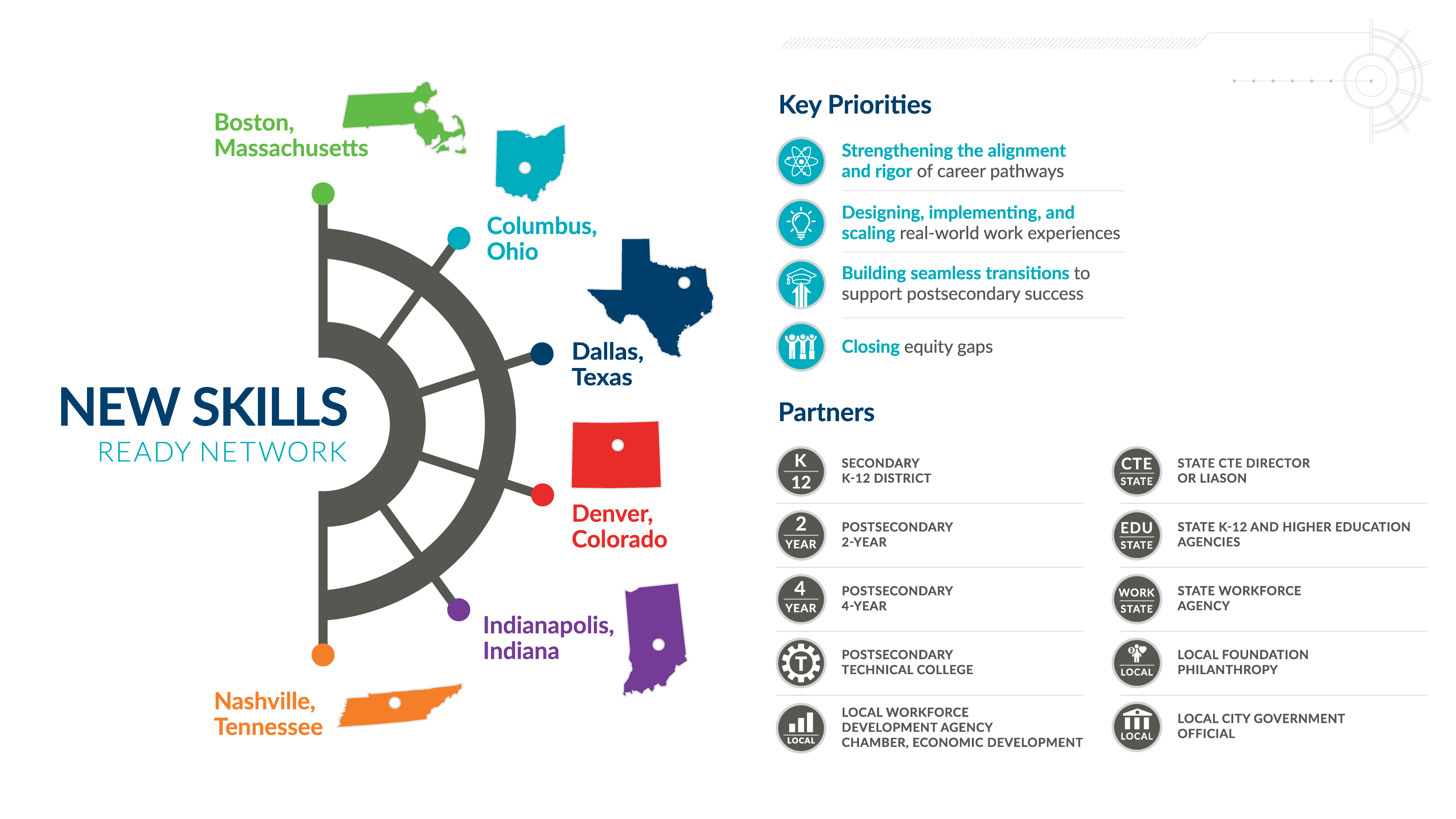
 Today, Advance CTE and Education Strategy Group (ESG) released an
Today, Advance CTE and Education Strategy Group (ESG) released an