This week, lawmakers returned to Capitol Hill for a brief work period ahead of the Thanksgiving holiday later this month. Following electoral victories in both chambers, Congressional Republicans held leadership elections while the White House and U.S. Department of Education (ED) celebrated efforts to connect education and careers.
Lame Duck Session Begins as Lawmakers Look to Next Year
 While results from last week’s general elections continue to be counted, the partisan balance of the 119th Congress has been formally determined. Republicans will retain control of the House, although the party’s margin of control—which may change further as President-Elect Trump continues to nominate individuals for key posts in his Administration—is still being determined. In the Senate, Republicans have at least a two-seat majority pending final Senate election results in Pennsylvania. These developments will have significant implications for federal Career Technical Education (CTE) policy and related funding in the coming years, which will come into sharper focus in the weeks and months ahead.
While results from last week’s general elections continue to be counted, the partisan balance of the 119th Congress has been formally determined. Republicans will retain control of the House, although the party’s margin of control—which may change further as President-Elect Trump continues to nominate individuals for key posts in his Administration—is still being determined. In the Senate, Republicans have at least a two-seat majority pending final Senate election results in Pennsylvania. These developments will have significant implications for federal Career Technical Education (CTE) policy and related funding in the coming years, which will come into sharper focus in the weeks and months ahead.
Lawmakers returned to Washington, D.C., this week to begin a short work period ahead of the Thanksgiving holiday later this month. Republican leadership in both Congressional chambers set about electing new leadership for the coming 119th Congress. In the House, Republicans unanimously elected current Speaker Mike Johnson (R-LA) to formally run for the position at the beginning of the 119th Congress next January. Current Majority Leader Steve Scalise (R-LA) and Majority Whip Tom Emmer (R-MN) were also elected to retain these leadership roles. Rep. Lisa McClain (R-MI) has also been elected as Republican Conference Chair, replacing outgoing Chair Elise Stefanik (R-NY), who was recently nominated to become the U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations.
In the Senate, Republicans elected Sen. John Thune (R-SD) to serve as the next Majority Leader. Thune will replace longtime Leader Mitch McConnell, who announced his plans to step down from leadership earlier this year. Sen. John Barrasso (R-WY) was elected as the next Senate Majority Whip, while Sen. Cotton (R-AR) was elected as Senate Republican Conference Chair.
Congressional Democrats are expected to hold similar leadership elections in the coming weeks. As these efforts and more continue to take shape, Advance CTE will continue to monitor and share these developments with the wider CTE community.
Advance CTE and Partners Submit First ICR Comments
As previously shared, the U.S. Department of Education (ED) recently issued a significant regulatory proposal that would, if enacted, impact the implementation of the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act (Perkins V). Advance CTE and the Association for Career and Technical Education (ACTE) have continued to voice significant concerns regarding this proposal and submitted a formal response to the proposal’s changes to Perkins V’s state plan guide earlier this week. Additional feedback related to proposed changes impacting the law’s Consolidated Annual Report (CAR) requirements is due on November 26.
White House Hosts Career Summit
On Wednesday, the White House and the U.S. Department of Education (ED) hosted a “Classroom to Careers” summit to bring together education and workforce leaders to celebrate the successes of the Biden-Harris Administration’s wider Investing in America agenda. The Summit highlighted progress in creating job opportunities and expanding the non-degree career pathways into critical sectors of the economy, including infrastructure, clean energy, advanced manufacturing, and more. The event culminated efforts from the Biden administration’s investments to bridge the gap between education and industry through high-quality career training programs and partnerships between educational institutions and employers. First Lady Dr. Jill Biden, in particular, highlighted that 34 states in recent years have advanced policies making the first two years of postsecondary education more affordable or free, among many other promising approaches to provide greater opportunities for learners.
Rob Young, Communications & Advocacy Associate
Steve Voytek, Policy Advisor



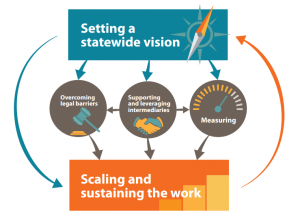 Once a statewide vision is in place and early implementation has begun, state policymakers should consider how to measure and scale work-based learning. There are two common approaches states take to building a comprehensive measurement and data-collection system: a systems-level approach that examines and evaluates the quality of the program, and a student-level approach that measures student learning and skill attainment. Through its
Once a statewide vision is in place and early implementation has begun, state policymakers should consider how to measure and scale work-based learning. There are two common approaches states take to building a comprehensive measurement and data-collection system: a systems-level approach that examines and evaluates the quality of the program, and a student-level approach that measures student learning and skill attainment. Through its