In September 2024, Advance CTE and ECMC Foundation announced the third cohort of The Postsecondary State Career Technical Education Leaders Fellowship at Advance CTE—Sponsored by ECMC Foundation (Fellowship). The Advance CTE — ECMCF Fellows include representation across multiple demographic categories reflecting the Fellowship’s goal of intentionally building a postsecondary leadership pipeline for underserved populations in Career Technical Education (CTE) that closes racial representation gaps and removes equity barriers to postsecondary leadership advancement.
This blog is part of the Fellow Feature series, highlighting the journeys and insights of leaders in the Fellowship. In this blog, Senior Policy Associate Vania Iscandari interviewed Fellow Cory Ortiz, Dean of the School of Career Education at the University of Alaska Southeast and incoming Division Director of Alaska Vocational Technical Center (AVTEC).
Q: Cory, you’ve had quite a remarkable journey in the field of CTE. Can you walk us through your story and how you ended up in this role as Dean of the School of Career Education?
 A: Absolutely. I come from a family that always emphasized the importance of education—my parents were determined that my brother and I would pursue higher education to secure better career opportunities. Originally, I thought engineering was my path, but as I progressed, I realized I had a passion for education. I shifted my focus and began teaching in high-poverty schools in Ogden, Utah, where I worked closely with Hispanic students. My goal was always to help them break the cycle of poverty and secure meaningful, well-paying jobs. That experience was pivotal—it shaped my belief in the power of education to change lives.
A: Absolutely. I come from a family that always emphasized the importance of education—my parents were determined that my brother and I would pursue higher education to secure better career opportunities. Originally, I thought engineering was my path, but as I progressed, I realized I had a passion for education. I shifted my focus and began teaching in high-poverty schools in Ogden, Utah, where I worked closely with Hispanic students. My goal was always to help them break the cycle of poverty and secure meaningful, well-paying jobs. That experience was pivotal—it shaped my belief in the power of education to change lives.
From there, I pursued advanced degrees, encouraged by a former advisor who saw potential in me. With each step, I gained a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities within the education system, particularly for students from diverse backgrounds. It’s been a journey of learning and growing, and now I have the privilege of leading a school that is focused on providing equitable access to career education.
Now, as a Fellow, I’m excited to connect with others in the field and continue to grow through collaboration, networking, and learning from the collective experience of my peers. The Fellowship has provided invaluable opportunities to reflect on how we can improve CTE at a systemic level, and it’s helping me sharpen my vision for the future.
Q: You’ve spoken before about your commitment to supporting marginalized learners. Can you share how this commitment has shaped your leadership and actions as a Dean?
A: One of the most significant moments in my career was when I made the decision not to accept funding for a wealthier school unless a comparable amount was allocated to a less resourced school in our district. It wasn’t an easy decision, but it was an important one. I have always believed that equity isn’t just about equal treatment—it’s about giving each student the resources and opportunities they need to succeed.
As a Dean, my focus is on ensuring that every student, especially those from underserved communities, has access to quality career and technical education. This includes working with Native and indigenous populations in Alaska, where I’m actively involved in shaping programs that are more culturally relevant and accessible. I’ve also learned that true equity requires listening to the community, engaging in dialogue, and being open to new ideas and approaches.
Through my work with the Fellowship, I’ve gained deeper insights into the challenges of advancing equity across the country and the ways we can collaborate to make meaningful changes.
Q: Speaking of Alaska, what do you see as the future of CTE in the state, and what challenges do you think need to be addressed?
A: The landscape of CTE in Alaska is evolving, but there’s still a lot of work to be done. One of the biggest challenges we face is the perception of CTE. Many still view it as a less academic path, which couldn’t be further from the truth. CTE programs are highly rigorous and offer students the skills they need to thrive in the workforce. But this perception needs to change—not just among students, but also among educators and school counselors. I’m working hard to ensure that CTE is recognized for its academic value and its relevance in preparing students for high-demand jobs.
Another issue is the lack of dual credit opportunities for students, which would allow them to earn both high school and college credits for CTE courses. This would significantly enhance their post-secondary education opportunities. And when it comes to Native students, we need a system that recognizes their unique cultural needs while providing equitable access to training programs.
We’re also considering conducting an equity audit to better understand the demographics of our programs and ensure they reflect the diversity of the students we serve. We’re at a point where we need to push for more equitable access, and that’s something I’m passionate about.
Q: There’s often a divide between “white-collar” professions and jobs in the skilled trades, especially when it comes to the guidance learners receive from school counselors. How do you address this misconception in CTE?
A: That’s a big issue, particularly in Alaska, where trade jobs—like construction management—are in high demand, and yet students are often steered toward what are seen as “cleaner” or “easier” white-collar jobs. The reality is that many trades, especially in fields like construction management, offer excellent compensation and career stability. These roles are highly technical and require significant education, which is why CTE programs are so crucial in providing the skills needed for these jobs.
Part of the challenge is getting students—and their parents—to understand that a career in the trades can be just as rewarding and prestigious as a white-collar job. We also need to give students early career guidance so they can make informed decisions. It’s about changing the narrative and showing students that the path to success isn’t one-size-fits-all.
Q: You’ve shared that your own background and heritage have played a role in shaping who you are today. Can you talk about how your heritage influences your work in CTE?
A: My parents came from modest backgrounds; they pushed my brother and me to pursue higher education so we could have better lives. While I initially pursued engineering, my journey eventually led me to education, and I’ve come to realize how much my upbringing shaped my values and commitment to supporting marginalized communities.
In terms of CTE, my experiences—both personal and professional—have given me a unique perspective. I understand the importance of community, of finding ways to bridge gaps in access, and the role that cultural relevance plays in education. It’s one of the reasons I’m so passionate about developing programs that work for diverse populations, particularly for Native students in Alaska.
Q: As you continue to lead in CTE, what role do you see mentorship playing in shaping the future of this field, especially for aspiring leaders and students from marginalized backgrounds?
A: Mentorship is everything. I wouldn’t be where I am today without the guidance of mentors who challenged me, encouraged me, and helped me grow. For students, mentorship helps them understand the realities of their chosen profession. It’s also critical for aspiring leaders, who need feedback and reflection to develop their leadership styles.
I’m a strong advocate for giving back to the community through mentorship. It’s essential for leaders to help foster the next generation of talent, particularly in fields like CTE, where students often come from marginalized backgrounds. By providing support, advice, and opportunities for hands-on learning, we can ensure that future leaders are equipped to continue driving change in this field.
Q: Cory, congratulations on your appointment as the Division Director of Alaska Vocational Technical Center (AVTEC)! Can you share more about AVTEC and what excites you most about this new role?
A: Thank you! AVTEC is Alaska’s premier technical training center, offering clock-hour-based programs in fields like maritime studies, industrial electronics, and construction. As Division Director, I have the privilege of serving as the head of the school, guiding it into its next chapter while ensuring it continues to meet the needs of students across the state.
What excites me most about this role is AVTEC’s statewide reach and its ability to create life-changing opportunities for Alaskans. From high-demand trades to specialized technical fields, AVTEC equips students with the skills to secure meaningful careers. I’m particularly eager to use this platform to address systemic barriers to access for students in Alaska’s remote villages. Through my fellowship project, I plan to assess those barriers and explore innovative solutions to ensure AVTEC is accessible to all Alaskans, regardless of geography.
It’s an incredible opportunity to combine my passion for education with AVTEC’s mission, and I’m looking forward to collaborating with the community to build on its legacy of success.
As Cory’s journey illustrates, the path to leadership in CTE is one shaped by a commitment to equity, empowerment, and community. His insights are just one example of the incredible work being done by the Fellows of the Fellowship. To learn more about Cory and other inspiring leaders in the Fellowship, visit the Advance CTE website, where you can discover how these changemakers are shaping the future of CTE across the nation.
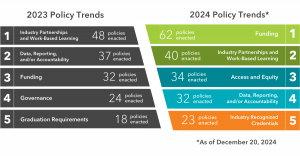
 To see more policy trends and access our policy tracker, check out the Advance CTE State Policy Resources page.
To see more policy trends and access our policy tracker, check out the Advance CTE State Policy Resources page.

 Meaningful learner engagement is critical to program improvement, equity, and inclusion across CTE programs, policies, and opportunities. Leaders across Vermont are well aware of the value of leveraging learner voice in CTE. Leaders across the conference elevated existing practices and opportunities to improve programs and learning environments and meet learners’ diverse needs using their feedback, input, and leadership.
Meaningful learner engagement is critical to program improvement, equity, and inclusion across CTE programs, policies, and opportunities. Leaders across Vermont are well aware of the value of leveraging learner voice in CTE. Leaders across the conference elevated existing practices and opportunities to improve programs and learning environments and meet learners’ diverse needs using their feedback, input, and leadership.  Session 2: Achieving Inclusive CTE Goal-Setting Through Data
Session 2: Achieving Inclusive CTE Goal-Setting Through Data To learn more about Advance CTE’s resources, supports, technical assistance and/or speaking opportunities,
To learn more about Advance CTE’s resources, supports, technical assistance and/or speaking opportunities, Hey y’all! My name is Brenna Bartlett, and I am beyond thrilled to join the Advance CTE team as the director of technical assistance. In this reimagined role, I’ll be working closely with members, states, and organizations to design and deliver tailored technical assistance that expands access to—and drives success in—high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). As a lifelong advocate for CTE, I couldn’t be more excited about the opportunity to collaborate with passionate leaders and learners from all across the country, working together to achieve even greater outcomes for our communities. Let’s get started!
Hey y’all! My name is Brenna Bartlett, and I am beyond thrilled to join the Advance CTE team as the director of technical assistance. In this reimagined role, I’ll be working closely with members, states, and organizations to design and deliver tailored technical assistance that expands access to—and drives success in—high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). As a lifelong advocate for CTE, I couldn’t be more excited about the opportunity to collaborate with passionate leaders and learners from all across the country, working together to achieve even greater outcomes for our communities. Let’s get started! A: Growing up, my family faced financial challenges, which made me acutely aware of the need for stable, well-paying jobs. For a while, I dreamt of becoming a journalist, but I quickly realized that CTE offered real, hands-on opportunities to build a sustainable career. What drew me to CTE wasn’t just financial stability; it was the chance to provide others, especially those from underserved communities, with the skills they need to succeed in today’s job market.
A: Growing up, my family faced financial challenges, which made me acutely aware of the need for stable, well-paying jobs. For a while, I dreamt of becoming a journalist, but I quickly realized that CTE offered real, hands-on opportunities to build a sustainable career. What drew me to CTE wasn’t just financial stability; it was the chance to provide others, especially those from underserved communities, with the skills they need to succeed in today’s job market.
 A:
A: Advance CTE recently held a panel on engaging employers at this year’s Fall Meeting, bringing together experts from education, industry, and workforce development to discuss how we can better align education and industry needs, create impactful partnerships, and prepare learners for the careers of tomorrow.
Advance CTE recently held a panel on engaging employers at this year’s Fall Meeting, bringing together experts from education, industry, and workforce development to discuss how we can better align education and industry needs, create impactful partnerships, and prepare learners for the careers of tomorrow. 
 In workforce development, education and industry partnerships help to align curriculum with industry needs, provide opportunities for real-world experience, and focus on skills over degrees to ensure that learners are not only ready for the workforce but are equipped to thrive in it.
In workforce development, education and industry partnerships help to align curriculum with industry needs, provide opportunities for real-world experience, and focus on skills over degrees to ensure that learners are not only ready for the workforce but are equipped to thrive in it. Since the fall of 2021, Advance CTE’s Opportunity Gap Analysis (OGA) workshop has provided training, resources, and support to help state leaders identify and address gaps in access to high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). To date, Advance CTE has led in-depth gap analysis training with 39 state teams from across the country. These teams have further disseminated the gap analysis process within their state CTE systems, resulting in changes in policies and practices that bring identifying and addressing gaps to the forefront of their CTE programs. This is the third post in a blog series where Senior Policy Associate, Jessi Maddox, interviews previous participants of the OGA workshop to share the impact and the lessons learned from implementing the training in their state.
Since the fall of 2021, Advance CTE’s Opportunity Gap Analysis (OGA) workshop has provided training, resources, and support to help state leaders identify and address gaps in access to high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE). To date, Advance CTE has led in-depth gap analysis training with 39 state teams from across the country. These teams have further disseminated the gap analysis process within their state CTE systems, resulting in changes in policies and practices that bring identifying and addressing gaps to the forefront of their CTE programs. This is the third post in a blog series where Senior Policy Associate, Jessi Maddox, interviews previous participants of the OGA workshop to share the impact and the lessons learned from implementing the training in their state.  The next cohort of the Opportunity Gap Analysis workshops will launch in the Spring of 2025. In this six-month cohort Advance CTE is providing training, resources and support to help state leaders identify and address gaps in access to high-quality
The next cohort of the Opportunity Gap Analysis workshops will launch in the Spring of 2025. In this six-month cohort Advance CTE is providing training, resources and support to help state leaders identify and address gaps in access to high-quality 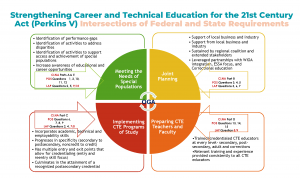

 As we look to the future of Career Technical Education (CTE), Advance CTE continues to support high-quality CTE programs created through legislation that addresses key challenges and opens new opportunities for learners and educators alike. In this blog, Policy Associate Velie Sando highlights recent state policies that can play a crucial role in shaping a more dynamic, accessible, and industry-aligned landscape.
As we look to the future of Career Technical Education (CTE), Advance CTE continues to support high-quality CTE programs created through legislation that addresses key challenges and opens new opportunities for learners and educators alike. In this blog, Policy Associate Velie Sando highlights recent state policies that can play a crucial role in shaping a more dynamic, accessible, and industry-aligned landscape. Dear State Career Technical Education (CTE) Leaders and Partners,
Dear State Career Technical Education (CTE) Leaders and Partners,