Many states, school districts and postsecondary institutions use labor market information (LMI) to justify the creation of new Career Technical Education (CTE) programs and to inform program design. This information, which includes data on the current and projected number of openings in specific industry sectors, as well as data on salary and any technological or policy advancements that may affect the Career Clusters®, can also be used at the state, regional, local and even student levels for career awareness and exploration in priority sectors.
However, the dissemination of LMI has often been carried out in an ad hoc and not a strategic way, hurting the effectiveness of the data itself. Today, Advance CTE released a guide about the effective dissemination of LMI, which will help states think through this process more strategically. The guide highlights work done in Nevada, Kentucky and Washington and their dissemination of LMI to employers, districts and learners, respectively, and poses guiding questions for states to consider for each of those audiences.
This guide was developed through the New Skills for Youth initiative, a partnership of the Council of Chief State School Officers, Advance CTE and Education Strategy Group, generously funded by JPMorgan Chase & Co.
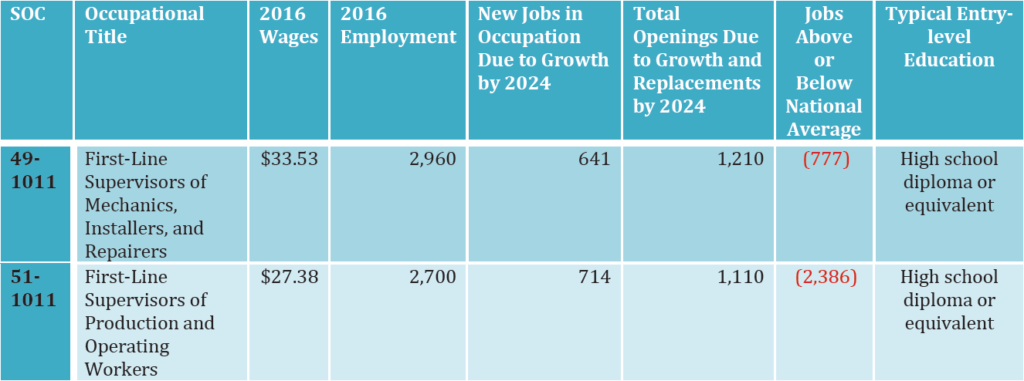
In Nevada, the state leveraged newly restructured Industry Sector Councils to create the 2017 In-Demand Occupations and Insights Report, which lists industries’ job growth and salary information for identified priority sectors along with a crosswalk for employers and CTE practitioners that identifies which occupation titles fall into which career pathways. This allows industry partners and CTE practitioners to communicate about LMI with a common language.
Kentucky similarly worked with industry partners to create a common language and used various data visualizations to share that information with school districts. When sharing LMI with district superintendents and CTE coordinators, the state was deliberate in how it presented the information so the LMI would have the most impact on policy with the least amount of confusion or varying interpretations.
Washington takes the state’s LMI straight to individual learners with Career Bridge, an online portal that allows students to explore career pathways and how they tie directly with job projections within the state. Additionally, the portal lists educational providers for specific career pathways and details student outcomes and other relevant data so that students have as much information as possible about their desired pathway.
All three of these state approaches disseminate LMI in various ways, but each is deliberate and thoughtful in both audience and messaging so that LMI can have the greatest positive effect for CTE programs. Read more about these strategies and examine your state’s approach by accessing the guide here.
Ashleigh McFadden, State Policy Manager


 A little over one year ago, Advance CTE launched
A little over one year ago, Advance CTE launched  In order to deliver high-quality CTE for all learners, state systems must work together at every level. Secondary and postsecondary must work together and with agencies that handle workforce and economic development issues. All of those agencies must also engage with employer partners and local districts and institutions to inform the design, validation and implementation of CTE programs.
In order to deliver high-quality CTE for all learners, state systems must work together at every level. Secondary and postsecondary must work together and with agencies that handle workforce and economic development issues. All of those agencies must also engage with employer partners and local districts and institutions to inform the design, validation and implementation of CTE programs. 
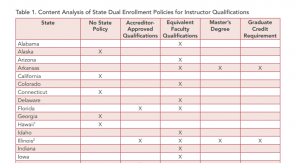 Many states allow students to earn credits in high school that can be applied towards a postsecondary degree or credential — a strategy known as dual, or concurrent, enrollment. While dual enrollment makes it easier and more affordable to obtain a postsecondary credential, states must pass policies to ensure students are receiving this advanced instruction from qualified teachers.
Many states allow students to earn credits in high school that can be applied towards a postsecondary degree or credential — a strategy known as dual, or concurrent, enrollment. While dual enrollment makes it easier and more affordable to obtain a postsecondary credential, states must pass policies to ensure students are receiving this advanced instruction from qualified teachers.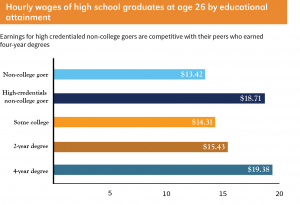 College is often considered a safe bet, but
College is often considered a safe bet, but  The report precedes an
The report precedes an  For students in high-skill career pathways, winning an invitation to the
For students in high-skill career pathways, winning an invitation to the