This month Tennessee Governor Bill Haslam’s vision for increasing postsecondary credential attainment in his state came one step closer to reality. On May 24, Gov. Haslam signed the Tennessee Reconnect Act into law, providing tuition scholarships for adult learners to access one of the state’s many community colleges and Colleges of Applied Technology. The Reconnect Act, a core piece of the Governor’s 2017 state of the state address, will be available to eligible non-degree holding adult students who are admitted into qualifying postsecondary institutions beginning in the fall of 2018.
The program is expected to have a substantial impact. The Tennessee General Assembly Fiscal Review Committee estimates that 5,503 additional part-time students and 4,102 full-time students will be eligible to receive the grant award in Fiscal Year 2018-19, at an estimated cost of $8.5 million.
Expanding access to postsecondary education and training has been a priority for Gov. Haslam during his tenure. In 2014, Tennessee launched the Tennessee Promise program, a last-dollar tuition scholarship that has seen tremendous growth and success since it was proposed in 2014. The state is seen as a pioneer in expanding access to free community college.
Separately, Gov. Haslam approved bills
- recognizing Oakland High School for winning the 2017 Excellence in Action award in the Manufacturing Career Cluster®;
- adopting the “Tennessee Tri-Star Scholar” designation to recognize students who graduate from high school with a composite score of 19 or higher on the ACTE, an equivalent score on the SAT, and a state-approved capstone industry certification;
- directing the Board of Regents and Higher Education Commission to develop postsecondary work-based learning curriculum and resources to assist in work-based learning training and placements; and
- Directing the State board of Education and the Department of Education to study other state systems of career preparation to identify opportunities to leverage flexibility under the Every Student Succeeds Act to better prepare Tennessee graduates for careers.
Coming Soon to Iowa Schools: New K-12 Computer Science Pathways
Meanwhile, Iowa passed a law to enhance digital literacy with new K-12 computer science standards and funding for teacher professional development. The legislature’s goal is that by July 2019, all elementary, middle and high schools in the state will offer some form of computer science instruction. The bill directs the Department of Education to establish a computer science education workgroup to put together a plan to adopt new graduation requirements, integrate computer science instruction into CTE pathways and develop new K-12 computer science pathways.
Additionally, the law establishes a computer science professional development incentive fund, which Governor Terry Branstad has proposed to fund at $500,000 in his 2019 budget. The fund is designed to help school districts pay for teachers to get additional training on computer science.
South Dakota Approves CTE Standards in Six Clusters
Speaking of standards, the South Dakota Board of Education voted in its May meeting to adopt new Career Technical Education (CTE) standards in six Career Clusters®: Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources; Arts, Audio-Video Technology and Communications; Finance; Health Science; Human Services; and Manufacturing. The standards were developed by workgroups of secondary CTE teachers, postsecondary faculty, industry representatives and others. Standards for five additional Career Clusters® will be developed later this summer.
Austin Estes, Policy Associate




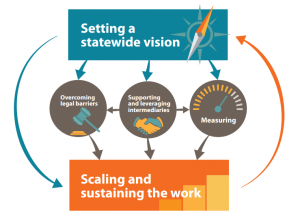 Once a statewide vision is in place and early implementation has begun, state policymakers should consider how to measure and scale work-based learning. There are two common approaches states take to building a comprehensive measurement and data-collection system: a systems-level approach that examines and evaluates the quality of the program, and a student-level approach that measures student learning and skill attainment. Through its
Once a statewide vision is in place and early implementation has begun, state policymakers should consider how to measure and scale work-based learning. There are two common approaches states take to building a comprehensive measurement and data-collection system: a systems-level approach that examines and evaluates the quality of the program, and a student-level approach that measures student learning and skill attainment. Through its  Work-based learning provides a continuum of activities — from career exploration and job shadowing to internships and apprenticeships — that help students develop technical and professional skills in an authentic work environment. While many work-based learning programs are designed and operated at the local level, several states have begun building a data collection and evaluation strategy to ensure program quality, identify and scale successful programs, and share promising practices. To support state efforts in this work, Advance CTE today released a brief that explores strategies for measuring work-based learning.
Work-based learning provides a continuum of activities — from career exploration and job shadowing to internships and apprenticeships — that help students develop technical and professional skills in an authentic work environment. While many work-based learning programs are designed and operated at the local level, several states have begun building a data collection and evaluation strategy to ensure program quality, identify and scale successful programs, and share promising practices. To support state efforts in this work, Advance CTE today released a brief that explores strategies for measuring work-based learning.