Last month, Advance CTE unveiled the newly modernized Career Clusters Framework at its 2024 Fall Meeting held in Phoenix, AZ, after two years of development and validation. This post is a recap of the unveiling of the new Framework and the reaction panel that followed during the Fall Meeting plenary session, a look at the path ahead, and resources to support awareness and implementation.
Introducing the Framework
Advance CTE’s 2024 Fall Meeting kicked off with the unveiling of the modernized National Career Clusters Framework, the primary organizing tool central building block to achieving consistently designed and high-quality Career Technical Education (CTE) programs and used in some form in the majority of states and territories across the United States.
Watch Introducing the Modernized National Career Clusters® Framework:
The original Career Clusters Framework, released in 2002, was designed to provide a more consistent design of CTE programs and more organized, sequenced paths to a career choice. The newly modernized Framework addresses concerns from the CTE community that the original Framework no longer represented the full world of work or the interdisciplinary careers and skills needed in the modern workforce. The modernized Framework is different but familiar, serving as a tool to bridge gaps between education and the workforce by setting a new standard for career exploration and preparation amid an evolving landscape. The modernized Framework has a next-level purpose: inclusive of all living-wage careers and areas of work, learner-centric to support exploration that leads to agency for learners deciding what career to embark on and learn skills for, and industry-responsive by using labor market information and industry language that can continue to be refreshed into the future of work.
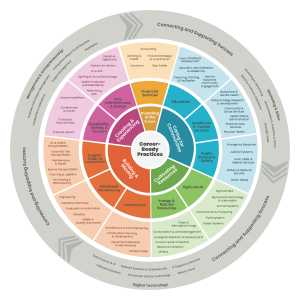 The modernized Career Clusters Framework wheel graphic (pictured right) visually represents the 14 Clusters and 72 Sub-Clusters that represent the world of work reorganized in the modernized framework. Three Cluster positions on the gray outer ring are identified as Cross-Cutting Clusters and can be standalone Clusters or be combined with other Clusters.
The modernized Career Clusters Framework wheel graphic (pictured right) visually represents the 14 Clusters and 72 Sub-Clusters that represent the world of work reorganized in the modernized framework. Three Cluster positions on the gray outer ring are identified as Cross-Cutting Clusters and can be standalone Clusters or be combined with other Clusters.
The Modernized National Career Clusters Framework Guidebook
The development of the Framework utilized input from over 4,000 members of the CTE community. Several of those perspectives were represented on a reaction panel following the introduction of the Framework by Advance CTE President Thalea Longhurst and Advance CTE. The following are reflections on the modernized Framework from education, career development, and industry representatives.

Pictured (left to right): Dr. Katie Graham (NE State CTE Director), Eva Mitchell (CEO, Coalition for Career Development), Trey Michael (NC State CTE Director), and Melissa Rekeweg (Managing Director, National Council for Agricultural Education; Associate Director, National FFA).
Emerging Themes in Initial Reactions
Eva Mitchell, CEO of the Coalition for Career Development Center, highlighted a consistent theme about how the design of the new Framework encourages New Mindsets for Connecting Conversations and Systems. She attested to the Framework’s value in drawing connections for learners and educators to the societal workforce, activating relevant, career-driven decisions and relevant instruction: “On a practical level, this Framework is like the missing piece of a puzzle that unites educators that support the building of career-ready skills that are technical and non-technical. I kind of see this as a Rosetta Stone document that can unite the conversations and practices between CTE educators, nontechnical skills, industry, and city spaces.”
Eva reflected on her work with career advisors, noting the difficult job of connecting high schoolers close to graduation to career pathways to long-term careers compared the Framework’s potential to support early-grade career advising: “This will really help the career advising and development work to potentially drill down in more places even down to the kindergarten level. Sometimes, educators only understand the pathways they’ve been exposed to, which aren’t in this range of 72 different modern career fields. It’ll give [learners] a big enough picture to understand how expansive the world [of work] is.”
Speakers also elevated the use of Cross-Cutting Clusters, purpose-driven Cluster Groupings, and flexible design of the Framework as a Reimagining of CTE Design and Delivery, empowering learners to take control of their learning and future careers. It also encourages state and local practitioners to imagine more interdisciplinary CTE programs across multiple Career Clusters. Melissa Rekeweg, the Managing Director of the National Council for Agricultural Education and Associate Director with the National FFA, remarked on the new learning opportunity: “[The new Framework] speaks to what students can do and their choices. This Cluster model is really allowing students to focus on what they want to do, allowing us the power to make that happen, and that flexibility is not just for the student but also for us to continue to mold it five, ten, fifteen years from now.”
The flexibility of the new Framework opens new doors for learners, CTE instructors, and educators. Trey Michael, North Carolina’s State CTE Director, reflected on the needs in his state and how the new Framework will expand access as instructors can become credentialed in more than one Career Cluster. He shared, “I started out in business, so when I came into education, I saw a bunch of silos. In the business world, you learn holistically; it’s less of a sequence of one thing at a time and more of ‘here’s a problem, let’s solve that problem.’ We have great specialized teachers in CTE, but how do we get them out of the silo?”.
As for Opportunities for Innovation, each panelist remarked on the modern nature of the Cross-Cutting Clusters and envisioned learners accessing skills that support continuous learning and career development after completing a program of study. As Trey put it, the opportunities for innovation and implementation could be tricky. Still, they will yield tremendous results if state leaders connect with local education and industry leaders to bring intention to implement the modernized Framework. He remarked, “I’m interested in the pain points, not just the large ones but the smaller ones that could be considered minor but have a longer timeline for thought and change.”
Looking Ahead
Advance CTE will continue to have opportunities for states to engage in Career Clusters Framework Adoption & Implementation. The new Framework becomes an important tool in the conversation to strengthen the education system at secondary and postsecondary institutions and the nation’s workforce and economy. This is no small task; we look forward to doing it together.
View the recording of Advance CTE’s October 30 webinar introducing the final modernized Framework.
Our Resources webpage will continue to be updated with materials for implementation at state and local levels, crosswalks, and communication tools to help leaders at every level assess, adopt, and implement the Framework at their pace and capacity.
Please reach out through our contact us form or via email at [email protected]
Rob Young, Communications & Advocacy Associate 



 In expanding access to college and career advising, Boston Public School members of the initiative’s
In expanding access to college and career advising, Boston Public School members of the initiative’s Implementing MyCAP with fidelity across Boston Public Schools requires sustainable and deepened staff capacity at the district’s central office as well as at the school level. Marsha and Erin both support cultivating and maintaining strategic partnerships across the district to align with MyCAP priorities. The collaboration and partnerships during this first year of expanded access to middle-grade learners included leveraging family liaisons who support informing learners and families of opportunities within Boston Public Schools and activating counselor teams that support caseloads of learners in the middle grades. The project team also expanded its reach to include community partnerships that operate in the college and career areas to better serve middle-grade learners. The advantage of bringing these partnerships into the fold allowed greater support for learners with exposure to skills and experiences that support college and career readiness and success (see image).
Implementing MyCAP with fidelity across Boston Public Schools requires sustainable and deepened staff capacity at the district’s central office as well as at the school level. Marsha and Erin both support cultivating and maintaining strategic partnerships across the district to align with MyCAP priorities. The collaboration and partnerships during this first year of expanded access to middle-grade learners included leveraging family liaisons who support informing learners and families of opportunities within Boston Public Schools and activating counselor teams that support caseloads of learners in the middle grades. The project team also expanded its reach to include community partnerships that operate in the college and career areas to better serve middle-grade learners. The advantage of bringing these partnerships into the fold allowed greater support for learners with exposure to skills and experiences that support college and career readiness and success (see image). 
 Maine offers two primary programs within their early college program offerings: the Dual Enrollment Career Technical Education Program and the Aspirations Program. A promising practice and important aspect of these programs is empowering local districts and CTE centers to choose the program and partner institution that best fits the needs of their learners.
Maine offers two primary programs within their early college program offerings: the Dual Enrollment Career Technical Education Program and the Aspirations Program. A promising practice and important aspect of these programs is empowering local districts and CTE centers to choose the program and partner institution that best fits the needs of their learners.



 Introduction
Introduction The first project I was assigned to involved the
The first project I was assigned to involved the  Over the last two weeks, the U.S. Secretary of Labor Marty Walsh testified before Congress on the U.S. Department of Labor’s (DOL) federal fiscal year 2023 (FY23) budget request while lawmakers in the House advanced FY23 appropriations legislation with implications for Career Technical Education (CTE) funding. Advance CTE also endorsed legislation aimed at promoting career awareness this week, while the Senate held a hearing on the pandemic’s impact on students’ learning. In addition, the Federal Communications Commission disbursed additional connectivity funds as part of a wider effort to provide affordable access to high-quality internet connections and devices, while the U.S. Department of Education (ED) published new rules for Title IX.
Over the last two weeks, the U.S. Secretary of Labor Marty Walsh testified before Congress on the U.S. Department of Labor’s (DOL) federal fiscal year 2023 (FY23) budget request while lawmakers in the House advanced FY23 appropriations legislation with implications for Career Technical Education (CTE) funding. Advance CTE also endorsed legislation aimed at promoting career awareness this week, while the Senate held a hearing on the pandemic’s impact on students’ learning. In addition, the Federal Communications Commission disbursed additional connectivity funds as part of a wider effort to provide affordable access to high-quality internet connections and devices, while the U.S. Department of Education (ED) published new rules for Title IX.  Today, Advance CTE and Education Strategy Group (ESG) released an annual report and site snapshots for year two of the
Today, Advance CTE and Education Strategy Group (ESG) released an annual report and site snapshots for year two of the 
 Boston, Massachusetts,
Boston, Massachusetts,