Without Limits: A Shared Vision for the Future of Career Technical Education (CTE Without Limits) was released in March 2020 with the support of over 40 national organizations. In October 2021, Advance CTE launched a technical assistance opportunity called Advancing CTE Without Limits, which sought to support states in a project to coordinate systems, improve equity goals, strengthen policy, or otherwise align with a CTE Without Limits principle. The year-long Advancing CTE Without Limits project ran from March 2022 to March 2023. This blog series shares the details, outcomes and lessons learned from projects across the three participating Pushing the Limits state teams – Colorado, Nebraska and South Carolina.
 Project Focus
Project Focus
Colorado has taken significant steps to improve equity in Career Technical Education (CTE), with a focus on ensuring that all students have access to high-quality CTE programs and opportunities.
The Colorado State CTE team made a concerted effort to better align their CTE Strategic Plan with the CTE Without Limits vision principles by conducting a review of their strategic plan through the lens of Principle 2: Each learner feels welcome in, is supported by and has the means to be successful in the career preparation ecosystem.
Colorado’s team focused on three key objectives:
- Needs Assessment: Conduct a needs assessment to identify strengths and gaps of the current CTE system and identify the CTE-specific actions that need to be taken to close gaps and remove barriers for learners.
- Internal, Equity-Focused Professional Development: Elevate the commitment at the state level to ensure equity within CTE through convening an internal team to develop a plan and participate in professional development on equity utilizing the Brave Dialogues resources.
- Building Local Leader Data Literacy: Leverage Advance CTE’s Opportunity Gap Analysis process to increase data literacy of local CTE administrators and educators and in doing so improve data-focused storytelling of learners’ outcome and identification of program participation and success gaps.
Project Outcomes
Through technical assistance sessions with Advance CTE staff, Colorado developed an equity strategy to help bridge the current CTE strategic plan and work on their next State Plan for the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act (expiring in 2024). Colorado has shared their equity plan and progress with local CTE Directors at a kickoff meeting where the Opportunity Gap Analysis process and Brave Dialogues training was conducted. Colorado will continue to create spaces to execute implementation of the plan grounded in Principle 2 at their CTE administrators’ convenings during this year.
Colorado established internal team-level goals around each action step within Principle 2 and embedded them into individual performance goals. The Colorado team elevated their focus on CTE program equity, access, and inclusion by settling on an overall goal that is connected to the state CTE strategic plan’s foundational elements and “job-specific” goals to promote a culture of shared growth around competency in equity.
Colorado launched the Opportunity Gap Analysis Workshop training and the Brave Dialogues equity training at The Colorado Association for Career & Technical Administrators (CACTA) conference. Colorado had an overwhelming response from the field about how much they appreciated being “called in” to the conversation and supported through professional development.
Colorado state CTE leaders continue to work towards advanced implementation of Principle 2 and were able to meet certain benchmarks over the course of the year:
- The Colorado CTE team provided feedback about their increased comfortability and feeling of competency to lead conversations and conduct a gap analysis that leads to achieving Principle 2: “Each learner feels welcome in, is supported by and has the means to be successful in the career preparation ecosystem.”
- Colorado achieved a more than 5 percent increase in work-based learning participation for learners who have identified as Black, American Indian or Alaskan Native, Asian/Pacific Islander and Latinx.
Lessons Learned
To address the identified gaps in CTE enrollment, Colorado is working on targeted marketing materials and campaigns to increase awareness about CTE to bolster the pipeline of interested learners. They have made tremendous strides with some school districts and colleges to address barriers to increase enrollment. Colorado is building a team of champions who can advocate for the importance of expanded access and equity for all learners in CTE and articulate the numerous benefits both for the state’s economy as well as for Colorado’s future workforce.
Colorado stressed that the sustainability of this work will be achieved through the continued utilization of the Opportunity Gap Analysis tools as part of Colorado’s Comprehensive Local Needs Assessment (CLNA) process and through building intentional linkages between Principle 2 work and the CTE strategic plan to further benchmark and establish goals tied to CTE data and local performance. Colorado’s team is also committed to work on their own language, implicit bias, personal and professional growth and development as equity-minded leaders.
Stay tuned for future updates about Colorado’s continued efforts or for more information about other states’ Advancing CTE Without Limits projects. For more information about CTE Without Limits, visit https://careertech.org/without-limits.
To learn more about planning and implementing the principles of CTE Without Limits in your state, check out Pushing the Limits: A Roadmap for Advancing CTE Without Limits.
Nithya Govindasamy, Senior Advisor


 In March 2021, Advance CTE released
In March 2021, Advance CTE released  Nebraska
Nebraska
 As part of ongoing blog topics aimed at supporting all learners in the realization of the national vision for the future of Career Technical Education (CTE),
As part of ongoing blog topics aimed at supporting all learners in the realization of the national vision for the future of Career Technical Education (CTE),  In March 2021, Advance CTE released
In March 2021, Advance CTE released  Once DSD administration began conversations with educators and staff, they recognized the need to create schoolwide “Without Limits Teams,” comprised of a school administrator, special education staff, school counselors, and the school’s CTE coordinator. Last spring, school staff from each of the 25 DSD schools were each brought together in full day district-wide workshops structured on the five CTE Without Limits principles and designed using Advance CTE’s
Once DSD administration began conversations with educators and staff, they recognized the need to create schoolwide “Without Limits Teams,” comprised of a school administrator, special education staff, school counselors, and the school’s CTE coordinator. Last spring, school staff from each of the 25 DSD schools were each brought together in full day district-wide workshops structured on the five CTE Without Limits principles and designed using Advance CTE’s 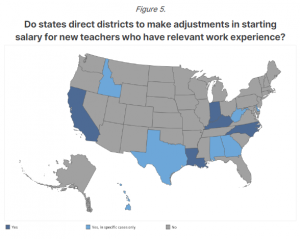
 On Friday, May 13, attendees at Advance CTE’s Spring State Leadership Retreat heard from three State CTE Directors participating in Advance CTE’s state cohort to begin implementation of
On Friday, May 13, attendees at Advance CTE’s Spring State Leadership Retreat heard from three State CTE Directors participating in Advance CTE’s state cohort to begin implementation of  Nebraska’s focus is advancin
Nebraska’s focus is advancin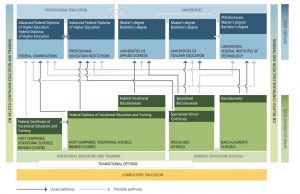
 Meet Kimberly Green! Kim is the Executive Director of Advance CTE. Kim’s role at Advance CTE is to provide strategic direction to all of the organization’s workstreams to ensure Advance CTE is boldly advancing toward the accomplishment of the strategic priorities and theory of action, both of which aspire to ensure equitable career success for each learner.
Meet Kimberly Green! Kim is the Executive Director of Advance CTE. Kim’s role at Advance CTE is to provide strategic direction to all of the organization’s workstreams to ensure Advance CTE is boldly advancing toward the accomplishment of the strategic priorities and theory of action, both of which aspire to ensure equitable career success for each learner.