Advance CTE’s 2023 Fall Meeting featured two rounds of interactive workshops based on the five foundation commitments of our vision, CTE Without Limits – equity, quality programs and instructors, public-private partnerships, and data and collaboration. These sessions allowed attendees to collaborate together to incubate innovative ideas in these specific topic areas and elevate Career Technical Education (CTE)’s impact in each state. Read our staff’s recaps and reflections on each workshop:
Foundational Commitment 1: Removing Geographic Barriers for Learners Through CTE Without Borders
Haley Wing, Senior Policy Associate
The Foundational Commitment 1 Workshop: Removing Geographic Barriers for Learners Through CTE Without Borders led participants through small and large group discussions and analysis to expand access within and across state borders.
 Jennell Ives, Director of the Secondary-Postsecondary Transitions Team at the Oregon Department of Education, offered a strategy for state teams working to expand access that includes an intensive two-day workshop. In this two-day workshop, she recommended states bring together cross-sector teams and champions across agencies to flesh through an action-planning process that addresses expanding statewide access to high-quality CTE and work-based learning opportunities across secondary and postsecondary institutions. Narrowing the time and space to solely focus on expanding access within and across state borders is a strategy to jump-start the work of expanding access and ensuring all partners, actions and responsibilities are aligned and actionable.
Jennell Ives, Director of the Secondary-Postsecondary Transitions Team at the Oregon Department of Education, offered a strategy for state teams working to expand access that includes an intensive two-day workshop. In this two-day workshop, she recommended states bring together cross-sector teams and champions across agencies to flesh through an action-planning process that addresses expanding statewide access to high-quality CTE and work-based learning opportunities across secondary and postsecondary institutions. Narrowing the time and space to solely focus on expanding access within and across state borders is a strategy to jump-start the work of expanding access and ensuring all partners, actions and responsibilities are aligned and actionable.
Foundational Commitment 2: Creating Opportunities with Stakeholders to Ensure Quality and Impact
Tunisha Hobson, Director, State Policy Implementation
Marcette Kilgore, Texas’ State CTE Director, introduced the process of engaging stakeholders in a program of study refresh which served as a catalyst for an implementation tour to ensure regions in the state were aware of changes to the state’s approved list of programs. The development process included the completion of a skills gap analysis, conducting listening tours, establishing statewide CTE advisory committees and offering and processing public comments through digital submissions. Participants learned about the use of a piloted software, Calibrate, a Skills Engine product created by the Center for Employability Outcomes within the Texas State Technical College System. The Calibrate system allowed employers to enter preferred skills by individual job profiles developed in alignment to the Department of Labor’s Standard Occupational Classification (SOC) codes.
The Texas Education Agency uploaded the course standards for every program of study which were created by grouping occupations by SOC code. An analysis of the alignment between course standards and industry-identified valuable skills was conducted to determine the gaps the agency needed to address as a priority and to schedule course reviews and rewrites/updates. The remainder of State Director Kilgore’s presentation focused on how this input was not limited to the pilot software but also included steps taken to engage the state’s CTE advisory committee, visit regions in the state and offer public comment opportunities which provided a more structured approach to supporting the redesign.
 Yolanda Flores, a member of the Postsecondary State CTE Leaders Fellowship at Advance CTE – Sponsored by ECMC Foundation, presented her real-world project focused on increasing adult learner awareness of opportunities available in manufacturing programs and subsequent in-demand high-wage jobs in Florida. She included an analysis of English Language Learners (ELL) and their access and supports while participating in the program. Her project includes an intervention through hosting a one-day exploration event for adult learners inclusive of ELL. The event not only increased awareness for the learner population, but it also identified for educators and industry partners other necessary interventions for addressing the needs of many more industries and learner groups. Flores was awarded a $170,000 grant to continue the work highlighted in her project to continue expanding access for learners.
Yolanda Flores, a member of the Postsecondary State CTE Leaders Fellowship at Advance CTE – Sponsored by ECMC Foundation, presented her real-world project focused on increasing adult learner awareness of opportunities available in manufacturing programs and subsequent in-demand high-wage jobs in Florida. She included an analysis of English Language Learners (ELL) and their access and supports while participating in the program. Her project includes an intervention through hosting a one-day exploration event for adult learners inclusive of ELL. The event not only increased awareness for the learner population, but it also identified for educators and industry partners other necessary interventions for addressing the needs of many more industries and learner groups. Flores was awarded a $170,000 grant to continue the work highlighted in her project to continue expanding access for learners.
Foundational Commitment 3: Advancing the National Career Clusters Framework
Paul Mattingly, Senior Policy Associate
Sheri Smith of Indigo Education Company and Alexandria Wright of WestEd’s Center for Economic Mobility provided an update on the National Career Clusters Framework Revision Project. The National Career Clusters® Framework is undergoing a modernization effort to ensure it remains responsive and relevant to both the world of work and learner needs for decades to come.
Participants in the workshop learned about the mixed method approach utilizing quantitative and qualitative methods for a data-informed process in updating the Framework. Additionally, participants learned of the progress that has been made recently with the Industry Advisory Groups and about the National Implementation Survey to gain knowledge about current and desired future use of the Framework and further support the engagement with those that use the Framework. During the group activities, attendees identified the most important uses and biggest challenges of utilizing the Framework for a variety of stakeholders.
Foundational Commitment 4: Data Dashboard Confessional – Ensuring Data are Actionable, Transparent and Trustworthy
Dan Adams, Associate Director, Data & Research
Dr. Jeffrey Fletcher, Lead Education Consultant at Iowa Department of Education, Bureau of Community Colleges and Postsecondary Readiness framed Iowa’s success with building and using Data Dashboards as involving three specific benchmarks: collaboration with grant recipients; collecting complete/correct data; and limitations such as data matching. The resulting data dashboards are allowing Iowa to monitor student outcomes from enrollment, through different levels of education, successful completion of education, and gainful employment.
 Donna Lewelling, Director at the Office of Community Colleges and Workforce Development at Oregon’s Higher Education Coordinating Commission described Oregon’s work standing up a postsecondary data dashboard. Critical to Oregon’s success has been building data literacy among those collecting and those using postsecondary CTE data. Oregon’s work is relational, and resources have been devoted to building and sustaining the relationships necessary to create useable data dashboards, as well as providing technical assistance to the field in using data to identify opportunities and obstacles to student success.
Donna Lewelling, Director at the Office of Community Colleges and Workforce Development at Oregon’s Higher Education Coordinating Commission described Oregon’s work standing up a postsecondary data dashboard. Critical to Oregon’s success has been building data literacy among those collecting and those using postsecondary CTE data. Oregon’s work is relational, and resources have been devoted to building and sustaining the relationships necessary to create useable data dashboards, as well as providing technical assistance to the field in using data to identify opportunities and obstacles to student success.
Foundational Commitment 5: Seamless Transitions: Continuously Improving Alignment Across Sectors
Eliza Fabillar, Senior Advisor
Alex Perry, Policy Advisor, Foresight Law and Policy, introduced the College in High School Alliance, a national partnership to advance dual enrollment and early college policy. Dual enrollment is growing nationwide, but more work is needed to develop consistent policies to achieve access to dual enrollment for all learners. States need to develop a common vision across sectors, expand the equity mission tied to dual enrollment by focusing on special populations, and be intentional about implementing policies that will advance dual enrollment. At the national level, policymakers and practitioners need to establish common definitions and examine policies and practices that support or hinder progress.
 Nancy Ligus, Advance CTE-ECMCF Fellow and Director of Workforce, Continuing Education and Economic Development at Pierpont Community College shared her work on a local workforce system. She differentiated systems versus ecosystems and provided a successful example from West Virginia. She also defined team characteristics that can ensure scalability and elaborated on strategies to form an ecosystem approach as a viable solution toward workforce and economic development goals.
Nancy Ligus, Advance CTE-ECMCF Fellow and Director of Workforce, Continuing Education and Economic Development at Pierpont Community College shared her work on a local workforce system. She differentiated systems versus ecosystems and provided a successful example from West Virginia. She also defined team characteristics that can ensure scalability and elaborated on strategies to form an ecosystem approach as a viable solution toward workforce and economic development goals.
Read our other blogs in the 2023 Fall Meeting recap series:


 Maine offers two primary programs within their early college program offerings: the Dual Enrollment Career Technical Education Program and the Aspirations Program. A promising practice and important aspect of these programs is empowering local districts and CTE centers to choose the program and partner institution that best fits the needs of their learners.
Maine offers two primary programs within their early college program offerings: the Dual Enrollment Career Technical Education Program and the Aspirations Program. A promising practice and important aspect of these programs is empowering local districts and CTE centers to choose the program and partner institution that best fits the needs of their learners.

 When was College in High School Alliance (CHSA) established and who were its founders? Was there a catalyst for its inception?
When was College in High School Alliance (CHSA) established and who were its founders? Was there a catalyst for its inception?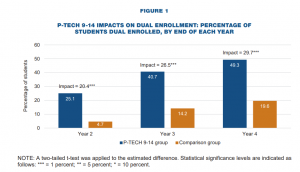 What findings from the Bridging of the School-to-Work Divide and the On-Ramp to College studies, would you highlight for state CTE leaders in particular
What findings from the Bridging of the School-to-Work Divide and the On-Ramp to College studies, would you highlight for state CTE leaders in particular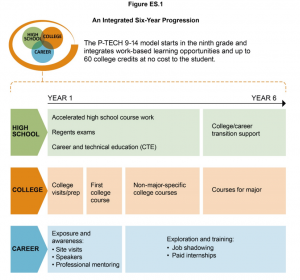



 Meet Christina Koch! Christina serves in the role of Policy Associate for Advance CTE. Christina works on projects related to state policy, including the New Skills
Meet Christina Koch! Christina serves in the role of Policy Associate for Advance CTE. Christina works on projects related to state policy, including the New Skills Two hallmarks of a high-quality career pathway are seamless transitions across secondary and postsecondary education and offering learners the opportunity and means to participate in early postsecondary opportunities (EPSOs) – which include dual enrollment, dual credit, concurrent enrollment and other related opportunities. It is critical that these opportunities seamlessly result in articulated postsecondary credit for learners in a degree program that will help them progress on their chosen career pathway with no hidden barriers.
Two hallmarks of a high-quality career pathway are seamless transitions across secondary and postsecondary education and offering learners the opportunity and means to participate in early postsecondary opportunities (EPSOs) – which include dual enrollment, dual credit, concurrent enrollment and other related opportunities. It is critical that these opportunities seamlessly result in articulated postsecondary credit for learners in a degree program that will help them progress on their chosen career pathway with no hidden barriers.