 Since the beginning of the year, over 35 governors have delivered their State of the State addresses, sharing their visions for the future of their state and highlighting educational priorities. Some addresses proposed to create new Career Technical Education (CTE) initiatives or increase funding for work-based learning, while others emphasized the importance of preparing students for their careers. In all, 24 addresses implicated CTE in some capacity, especially in the areas of workforce development, work-based learning and funding.
Since the beginning of the year, over 35 governors have delivered their State of the State addresses, sharing their visions for the future of their state and highlighting educational priorities. Some addresses proposed to create new Career Technical Education (CTE) initiatives or increase funding for work-based learning, while others emphasized the importance of preparing students for their careers. In all, 24 addresses implicated CTE in some capacity, especially in the areas of workforce development, work-based learning and funding.
Workforce Development
Speeches most commonly addressed workforce development at all learner levels which, considering states’ strategies for economic recovery, comes as no surprise. At the secondary level, Missouri Governor Mike Parson set a goal of 12,000 high school students with the WorkKeys Certification, calling the program an “important stepping stone for students who are not immediately college bound but have the knowledge and skills to fill high-demand jobs.” Kentucky Governor Andy Beshear announced the creation of the Better Kentucky Promise Program, a postsecondary-focused initiative to help over 6,000 Kentucky residents complete associate degrees or secure industry-recognized certificates. At the adult level, Governor Greg Gianforte of Montana announced the establishment of the Montana Trades Education Credit, which subsidizes businesses through scholarships up to 50% of the cost of upskilling or reskilling employees, and highlighted the Missouri One Start program, which has trained over 100,000 adults through 400 employer training partnerships.
Work-Based Learning
Many governors highlighted the importance of work-based learning initiatives in providing secondary students with career-ready skills. Governor Kim Reynolds of Iowa applauded efforts to integrate work-based learning into the K-12 curriculum and called on legislators to make work-based learning an expectation in all Iowa schools. Governor Brad Little similarly highlighted the role of work-based learning in Idaho, committing to further connecting students and employers for on-the-job experiences and professional skill development. Alaska Governor Mike Dunleavy also called for an expansion in this area, directing the Alaska Department of Education to create an apprenticeship program allowing secondary students to receive credit while working for local employers.
Funding and New Initiatives
Announcements of new or proposed funding also featured prominently across many speeches. South Carolina Governor Henry McMaster proposed $97 million for high-demand job skills training and workforce scholarships and grants to improve access to skills-based certificates. Governor Bill Lee of Tennessee highlighted the Governor’s Investment in Vocational Education (GIVE) Act, which consisted of $25 million in grants for 28 projects focused on CTE program expansion, and proposed a $10 million expansion for ten new sites, prioritizing economically disadvantaged communities. North Dakota Governor Doug Borgum advocated for $45 million allocated to supporting the expansion and development of successful CTE centers through matched grants, while South Dakota Governor Kristi Noem announced the Build Dakota Scholarship, a five-year, $40 million investment to match students with high-demand career opportunities. Investment in access to and expansion of CTE programming and training remains a clear priority nationwide.
Outside of CTE related areas, governors also focused heavily on equity in education, including highlighting how COVID-19 has disproportionately exacerbated achievement gaps for communities of color and allocating additional funding for expansion of broadband to students still participating in virtual learning. Advance CTE will continue to monitor the State of the State Addresses as they happen for their relevance to CTE.
Additional resources can be found in our Learning that Works Resource Center.
Dan Hinderliter, Policy Associate



 2018 was a significant year for Career Technical Education (CTE) at the federal and state levels. On July 31, 2018, the President signed the Strengthening Career and Technical Education for the 21st Century Act (Perkins V) into law, which reauthorized the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act of 2006 (Perkins IV). The reauthorization of Perkins signaled a federal commitment to and a recognition of the promise and value of high-quality CTE. Additionally, at the state level 42 states and Washington, D.C., passed a total of 146 policy actions related to CTE and career readiness, reflecting a commitment from state leaders to advance CTE.
2018 was a significant year for Career Technical Education (CTE) at the federal and state levels. On July 31, 2018, the President signed the Strengthening Career and Technical Education for the 21st Century Act (Perkins V) into law, which reauthorized the Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act of 2006 (Perkins IV). The reauthorization of Perkins signaled a federal commitment to and a recognition of the promise and value of high-quality CTE. Additionally, at the state level 42 states and Washington, D.C., passed a total of 146 policy actions related to CTE and career readiness, reflecting a commitment from state leaders to advance CTE. While roughly one hundred fewer policies were passed in 2018 than in 2017, this past year’s policies still reflect a commitment from state leaders to advance CTE. A decrease in the number of CTE policies passed compared to previous years should not be misinterpreted as an indication that CTE is not a priority for states. In fact,
While roughly one hundred fewer policies were passed in 2018 than in 2017, this past year’s policies still reflect a commitment from state leaders to advance CTE. A decrease in the number of CTE policies passed compared to previous years should not be misinterpreted as an indication that CTE is not a priority for states. In fact,  Digital literacy and computer science skills are increasingly necessary for success in today’s workforce, even in fields that are not directly related to information technology. As such, state leaders are recognizing the role that a robust computer science education strategy plays in preparing learners for their future careers and numerous states passed policies related to computer science during their 2018 legislative sessions.
Digital literacy and computer science skills are increasingly necessary for success in today’s workforce, even in fields that are not directly related to information technology. As such, state leaders are recognizing the role that a robust computer science education strategy plays in preparing learners for their future careers and numerous states passed policies related to computer science during their 2018 legislative sessions. Earlier this summer, Advance CTE in partnership with Education Strategy Group (ESG) and the Council of Chief State School Officers (CCSSO), released
Earlier this summer, Advance CTE in partnership with Education Strategy Group (ESG) and the Council of Chief State School Officers (CCSSO), released  The report found that criteria for qualifying Career Technical Education (CTE) instructors are mentioned in state-level policies in eight states (Colorado, Illinois, Kansas, Maine, Missouri, Mississippi, Ohio, Virginia). Dual enrollment teacher qualification policies are generally related to education attainment level, but exemptions are sometimes made for CTE dual enrollment instructors. In some of these cases, states allow exemption from qualification rules when instructors can demonstrate proficiency in the field they will teach and consider industry recognized credentials and years of experience working in the field when determining teacher qualifications.
The report found that criteria for qualifying Career Technical Education (CTE) instructors are mentioned in state-level policies in eight states (Colorado, Illinois, Kansas, Maine, Missouri, Mississippi, Ohio, Virginia). Dual enrollment teacher qualification policies are generally related to education attainment level, but exemptions are sometimes made for CTE dual enrollment instructors. In some of these cases, states allow exemption from qualification rules when instructors can demonstrate proficiency in the field they will teach and consider industry recognized credentials and years of experience working in the field when determining teacher qualifications.
 State Name: Missouri
State Name: Missouri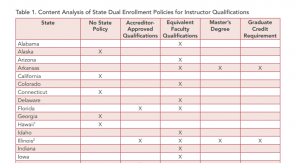 Many states allow students to earn credits in high school that can be applied towards a postsecondary degree or credential — a strategy known as dual, or concurrent, enrollment. While dual enrollment makes it easier and more affordable to obtain a postsecondary credential, states must pass policies to ensure students are receiving this advanced instruction from qualified teachers.
Many states allow students to earn credits in high school that can be applied towards a postsecondary degree or credential — a strategy known as dual, or concurrent, enrollment. While dual enrollment makes it easier and more affordable to obtain a postsecondary credential, states must pass policies to ensure students are receiving this advanced instruction from qualified teachers.